Syndromic Hydrocephalus
- PMID: 34801143
- PMCID: PMC8985913
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nec.2021.09.006
Syndromic Hydrocephalus
Abstract
Hydrocephalus, the abnormal accumulation and impaired circulation/clearance of cerebrospinal fluid, occurs as a common phenotypic feature of a diverse group of genetic syndromes. In this review, we outline the genetic mutations, pathogenesis, and accompanying symptoms underlying syndromic hydrocephalus in the context of: L1 syndrome, syndromic craniosynostoses, achondroplasia, NF 1/2, Down's syndrome, tuberous sclerosis, Walker-Warburg syndrome, primary ciliary dyskinesia, and osteogenesis imperfecta. Further, we discuss emerging genetic variants associated with syndromic hydrocephalus.
Keywords: Hydrocephalus; Hydrocephalus genetics; Syndromic hydrocephalus.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors have nothing to disclose.
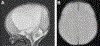
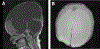
Figures

References
-
- Stumpel C, Vos YJ. Syndrome L1.In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al.,eds.GeneReviews®. University of Washington, Seattle; 1993. Accessed January 10, 2021. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1484/
-
- Adle-Biassette H, Saugier-Veber P, Fallet-Bianco C,et al.. Neuropathological review of 138 cases genetically tested for X-linked hydrocephalus: evidence for closely related clinical entities of unknown molecular bases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2013;126(3):427–442. doi:10.1007/s00401-013-1146-1 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

