Alcohol, inflammation, and blood-brain barrier function in health and disease across development
- PMID: 34801170
- PMCID: PMC9204474
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.irn.2021.06.009
Alcohol, inflammation, and blood-brain barrier function in health and disease across development
Abstract
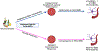
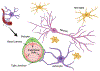
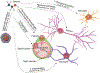
Alcohol is the most commonly used drug of abuse in the world and binge drinking is especially harmful to the brain, though the mechanisms by which alcohol compromises overall brain health remain somewhat elusive. A number of brain diseases and pathological states are accompanied by perturbations in Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) function, ultimately exacerbating disease progression. The BBB is critical for coordinating activity between the peripheral immune system and the brain. Importantly, BBB integrity is responsive to circulating cytokines and other immune-related signaling molecules, which are powerfully modulated by alcohol exposure. This review will highlight key cellular components of the BBB; discuss mechanisms by which permeability is achieved; offer insight into methodological approaches for assessing BBB integrity; and forecast how alcohol-induced changes in the peripheral and central immune systems might influence BBB function in individuals with a history of binge drinking and ultimately Alcohol Use Disorders (AUD).
Keywords: Adolescence; Alcohol; Blood-brain barrier; Cytokines; Inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott NJ, Ronnback L & Hansson E Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci 7, 41–53 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Alfonso-Loeches S, Urena-Peralta J, Morillo-Bargues MJ, Gomez-Pinedo U & Guerri C Ethanol-Induced TLR4/NLRP3 Neuroinflammatory Response in Microglial Cells Promotes Leukocyte Infiltration Across the BBB. Neurochem Res 41, 193–209 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

