Value of Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in the Prognosis Assessment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients: A Retrospective, Multicentre Cohort Study
- PMID: 34802005
- PMCID: PMC9153340
- DOI: 10.1159/000519750
Value of Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in the Prognosis Assessment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients: A Retrospective, Multicentre Cohort Study
Abstract
Introduction: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is one of the most common chronic diseases associated with high mortality. Previous studies suggested a prognostic role for peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) assessed during cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) in patients with COPD. However, most of these studies had small sample sizes or short follow-up periods, and despite their relevance, CPET parameters are not included in the Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) tool for assessment of severity.
Objectives: We therefore aimed to assess the prognostic value of CPET parameters in a large cohort of outpatients with COPD.
Methods: In this retrospective, multicentre cohort study, medical records of patients with COPD who underwent CPET during 2004-2017 were reviewed and demographics, smoking habits, GOLD grade and category, exacerbation frequency, dyspnoea score, lung function measurements, and CPET parameters were documented. Relationships with survival were evaluated using Kaplan-Meier analysis, Cox regression, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
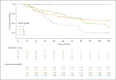
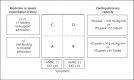
Results: Of a total of 347 patients, 312 patients were included. Five-year and 10-year survival probability was 75% and 57%, respectively. VO2peak significantly predicted survival (hazard ratio: 0.886 [95% confidence interval: 0.830; 0.946]). The optimal VO2peak threshold for discrimination of 5-year survival was 14.6 mL/kg/min (area under ROC curve: 0.713). Five-year survival in patients with VO2peak <14.6 mL/kg/min versus ≥ 14.6 mL/kg/min was 60% versus 86% in GOLD categories A/B and 64% versus 90% in GOLD categories C/D.
Conclusions: We confirm that VO2peak is a highly significant predictor of survival in COPD patients and recommend the incorporation of VO2peak into the assessment of COPD severity.
Keywords: All-cause mortality; Cardiopulmonary exercise testing; Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Lung function; Prognosis.
© 2021 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
R.E. received honoraria for scientific lectures from Actelion, GSK, United Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Berlin-Chemie, Boehringer Ingelheim, and OMT, and research funding from Boehringer Ingelheim and Actelion, Germany. M.H. received personal fees for lectures and consultations and travel, accommodation, and/or meeting expenses from Actelion, AOPOrphan/OMT, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Berlin-Chemie, Boehringer, GILEAD, GSK, MSD, Novartis, and Pfizer. G.H. received honoraria for scientific lectures from GSK, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Berlin-Chemie, and Boehringer Ingelheim. S.G. received honoraria for scientific lectures from AstraZeneca, Novartis, Berlin-Chemie, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Roche. A.O., A.Mü, J.W., B.T., A.Ho, M.W., A.He, A.Ma, B.S: No potential conflict of interest to report.
Figures






References
-
- Soriano JB, Abajobir AA, Abate KH, Abera SF, Agrawal A, Ahmed MB, et al. Global, regional, and national deaths, prevalence, disability-adjusted life years, and years lived with disability for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet Respir Med. 2017;5((9)):691–706. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease . Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (2020 report) Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease; 2020. Available from: https://goldcopd.org/gold-reports/
-
- Mannino DM, Thorn D, Swensen A, Holguin F. Prevalence and outcomes of diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular disease in COPD. Eur Respir J. 2008;32((4)):962–9. - PubMed
-
- Sode BF, Dahl M, Nordestgaard BG. Myocardial infarction and other co-morbidities in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a Danish nationwide study of 7.4 million individuals. Eur Heart J. 2011;32((19)):2365–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

