Structure-activity relationships for 5F-MDMB-PICA and its 5F-pentylindole analogs to induce cannabinoid-like effects in mice
- PMID: 34802041
- PMCID: PMC8882184
- DOI: 10.1038/s41386-021-01227-8
Structure-activity relationships for 5F-MDMB-PICA and its 5F-pentylindole analogs to induce cannabinoid-like effects in mice
Abstract
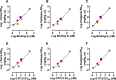
Synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists (SCRAs) are an evolving class of new psychoactive substances found on recreational drug markets worldwide. The indole-containing compound, 5F-MDMB-PICA, is a popular SCRA associated with serious medical consequences, including overdose and hospitalizations. In vitro studies reveal that 5F-MDMB-PICA is a potent agonist at cannabinoid type 1 receptors (CB1), but little information exists regarding in vivo pharmacology of the drug. To this end, we examined the in vitro and in vivo cannabinoid-like effects produced by 5F-MDMB-PICA and related 5F-pentylindole analogs with differing composition of the head group moiety (i.e., 5F-NNEI, 5F-SDB-006, 5F-CUMYL-PICA, 5F-MMB-PICA). In mouse brain membranes, 5F-MDMB-PICA and its analogs inhibited binding to [3H]rimonabant-labeled CB1 and displayed agonist actions in [35S]GTPγS functional assays. 5F-MDMB-PICA exhibited the highest CB1 affinity (Ki = 1.24 nM) and functional potency (EC50 = 1.46 nM), but head group composition markedly influenced activity in both assays. For example, the 3,3-dimethylbutanoate (5F-MDMB-PICA) and cumyl (5F-CUMYL-PICA) head groups engendered high CB1 affinity and potency, whereas a benzyl (5F-SDB-006) head group did not. In C57BL/6J mice, all 5F-pentylindole SCRAs produced dose- and time-dependent hypothermia, catalepsy, and analgesia that were reversed by rimonabant, indicating CB1 involvement. In vitro Ki and EC50 values were positively correlated with in vivo ED50 potency estimates. Our findings demonstrate that 5F-MDMB-PICA is a potent SCRA, and subtle alterations to head group composition can have profound influence on pharmacological effects at CB1. Importantly, measures of CB1 binding and efficacy in mouse brain tissue seem to accurately predict in vivo drug potency in this species.
© 2021. This is a U.S. government work and not under copyright protection in the U.S.; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Figures



References
-
- UNODC. United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime Early Warning Advisory Current NPS Threats - Volume III. 2020. https://www.unodc.org/documents/scientific/Current_NPS_Threats_Vol.4.pdf.
-
- Banister SD, Arnold JC, Connor M, Glass M, McGregor IS. Dark classics in chemical neuroscience: δ(9)-tetrahydrocannabinol. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2019;10:2160–75.. - PubMed
-
- Worob A, Wenthur C. DARK classics in chemical neuroscience: synthetic cannabinoids (Spice/K2) ACS Chem Neurosci. 2020;11:3881–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

