Severe Skin Toxicity Caused by Sequential Anti-PD-1 Antibody and Alectinib in Non-small-cell Lung Cancer: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review
- PMID: 34803090
- PMCID: PMC9259316
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.7472-21
Severe Skin Toxicity Caused by Sequential Anti-PD-1 Antibody and Alectinib in Non-small-cell Lung Cancer: A Report of Two Cases and a Literature Review
Abstract
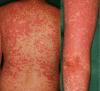
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have demonstrated marked efficacy in some cancer patients, but they may cause various severe immune-related adverse events. Alectinib is a second-generation anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) approved for ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Alectinib is said to be safer than other TKIs. We conducted an investigator-initiated trial of alectinib, which also has RET kinase-inhibitory activity, against RET-rearranged NSCLC. Two RET-rearranged NSCLC patients experienced severe skin toxicity with alectinib after first undergoing anti-PD-1 antibody treatment with an ICI. These findings suggest that we should carefully follow patients for adverse effects of targeted drugs following ICI treatment.
Keywords: ICIs; alectinib; anti-PD-1 antibody; severe skin toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
ALTA-2: Phase II study of brigatinib in patients with ALK-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer who progressed on alectinib or ceritinib.Future Oncol. 2021 May;17(14):1709-1719. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-1119. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Future Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33569983
-
Rapid and dramatic response to alectinib in an anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer patient who is critically ill.Anticancer Drugs. 2016 Jul;27(6):573-5. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000356. Anticancer Drugs. 2016. PMID: 26938871
-
Alectinib for the treatment of pretreated RET-rearranged advanced NSCLC: Results of the ETOP ALERT-lung trial.Lung Cancer. 2022 Oct;172:94-99. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.08.008. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Lung Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36030612 Clinical Trial.
-
Mixed responses to first-line alectinib in non-small cell lung cancer patients with rare ALK gene fusions: A case series and literature review.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Oct;25(19):9476-9481. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16897. Epub 2021 Sep 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34541785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Safety of alectinib for the treatment of metastatic ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer.Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017 Apr;16(4):509-514. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2017.1299706. Epub 2017 Mar 3. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2017. PMID: 28276856 Review.
Cited by
-
Rare MYH9-ROS1 Fusion Gene-Positive Lung Adenocarcinoma Showing Response to Entrectinib Treatment: A Case Study.Case Rep Oncol. 2022 Mar 31;15(1):376-381. doi: 10.1159/000524071. eCollection 2022 Jan-Apr. Case Rep Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35529286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hida T, Nokihara H, Kondo M, et al. . Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): an open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 390: 29-39, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Peters S, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, et al. . Alectinib versus crizotinib in untreated ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 377: 829-838, 2017. - PubMed
-
- Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, et al. . First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med 371: 2167-2177, 2014. - PubMed

