A New Strategy for the Rapid Identification and Validation of the Direct Targets of Aconitine-Induced Cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 34803375
- PMCID: PMC8599306
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S335461
A New Strategy for the Rapid Identification and Validation of the Direct Targets of Aconitine-Induced Cardiotoxicity
Abstract
Background: The interaction of small molecules with direct targets constitutes the molecular initiation events of drug efficacy and toxicity. Aconitine, an active compound of the Aconitum species, has various pharmacological effects but is strongly toxic to the heart. The direct targets of aconitine-induced cardiotoxicity remain unclear.
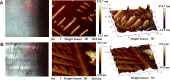
Methods: We predicted the toxic targets of aconitine based on network pharmacology and followed a novel proteomic approach based on the "drug affinity responsive target stability" technology combined with LC-MS/MS to identify the direct targets of aconitine. The identified targets were analysed from the perspective of multilevel and multidimensional bioinformatics through a network integration method. The binding sites were investigated via molecular docking to explore the toxicity mechanism and predict the direct targets of aconitine. Finally, atomic force microscopy (AFM) imaging was performed to verify the affinity of aconitine to the direct targets.
Results: PTGS2, predicted by network pharmacology as a toxic target, encodes cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), which is closely related to myocardial injury. Furthermore, cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2) is the upstream signal protein of PTGS2, and it is a key enzyme in the metabolism of arachidonic acid during an inflammatory response. We determined cPLA2 as a direct target, and AFM imaging verified that aconitine could bind to cPLA2 well; thus, aconitine may cause the expression of PTGS2/COX-2 and release inflammatory factors, thereby promoting myocardial injury and dysfunction.
Conclusion: We developed a complete set of methods to predict and verify the direct targets of aconitine, and cPLA2 was identified as one. Overall, the novel strategy provides new insights into the discovery of direct targets and the molecular mechanism of toxic components that are found in traditional Chinese medicine.
Keywords: aconitine; atomic force microscopy; cardiotoxicity; direct targets; drug affinity responsive target stability technology.
© 2021 Wei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Computational Exploration of Natural Compounds to Target Cytosolic Phospholipase A 2 Protein: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Spinal Cord Injury.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2018;14(2):117-124. doi: 10.2174/1573409914666180123100714. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2018. PMID: 29359676
-
Assessment of in vitro cardiotoxicity of extract fractions and diterpene alkaloids from Aconitum leucostomum Worosch: A short communication.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017 Apr 15;137:84-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.01.003. Epub 2017 Jan 3. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017. PMID: 28104561
-
Stepwise rapid tracking strategy to identify active molecules from Ixeris sonchifolia Hance based on "'affinity mass spectrometry-atomic force microscopy imaging'" technology.Talanta. 2020 Sep 1;217:121031. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121031. Epub 2020 Apr 15. Talanta. 2020. PMID: 32498901
-
Cardiac efficacy and toxicity of aconitine: A new frontier for the ancient poison.Med Res Rev. 2021 May;41(3):1798-1811. doi: 10.1002/med.21777. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Med Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 33512023 Review.
-
Aconite poisoning.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2009 Apr;47(4):279-85. doi: 10.1080/15563650902904407. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2009. PMID: 19514874 Review.
Cited by
-
A new paradigm for drug discovery in the treatment of complex diseases: drug discovery and optimization.Chin Med. 2025 Mar 24;20(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01075-4. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40122800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aconitine and its derivatives: bioactivities, structure-activity relationships and preliminary molecular mechanisms.Front Chem. 2024 Jan 22;12:1339364. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1339364. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38318112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aconitine in Synergistic, Additive and Antagonistic Approaches.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Oct 27;16(11):460. doi: 10.3390/toxins16110460. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39591215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Omics on Traditional Medicinal Plant of the Genus Aconitum: Current Progress and Prospect.Molecules. 2024 Dec 31;30(1):118. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010118. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39795175 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of Untargeted Metabolomics, Network Pharmacology, Single-Cell RNA Sequencing, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Reveals GOT1, CYP1A2, and CA2 as Potential Targets of Huang Qin Decoction Preventing Colorectal Cancer Liver Metastasis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 17;18(7):1052. doi: 10.3390/ph18071052. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40732339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese pharmacopeia. China Med Sci Press. 2020;Part I:40, 200, 247.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

