Novel approaches for COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment: a nonsystematic review
- PMID: 34803440
- PMCID: PMC8573842
- DOI: 10.3906/biy-2105-45
Novel approaches for COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment: a nonsystematic review
Abstract
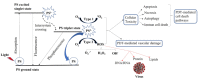
Since COVID-19 pandemic has been continuously rising and spreading, several original contributions and review articles on COVID-19 started to appear in the literature. The review articles are mainly focus on the current status of the pandemic along with current status of the corona diagnosis and treatment process. Due to some disadvantages of the currently used methods, the improvement on the novel promising diagnosis and treatment methods of corona virus is very important issue. In this review, after briefly discussing the status of current diagnosis and treatment methods, we present to the scientific community, novel promising methods in the diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19. As with other novel approaches, first, the diagnosis potential of mass spectroscopy and optical spectroscopic methods such as UV/visible, infrared, and Raman spectroscopy coupled with chemometrics will be discussed for the corona virus infected samples based on the relevant literature. In vibrational spectroscopy studies, due to complexity of the data, multivariate analysis methods are also applied to data. The application of multivariate analysis tools that can be used to extract useful information from the data for diagnostic and characterisation purposes is also included in this review. The reviewed methods include hierarchical cluster analysis, principal component analysis, linear and quadratic discriminant analysis, support vector machine algorithm, and one form of neural networks namely deep learning method. Second, novel treatment methods such as photodynamic therapy and the use of nanoparticles in the in-corona virus therapy will be discussed. Finally, the advantages of novel promising diagnosis and treatment methods in COVID-19, over standard methods will be discussed. One of the main aims of this paper is to encourage the scientific community to explore the potential of this novel tools for their use in corona virus characterization, diagnosis, and treatment.
Keywords: COVID-19; Raman spectroscopy; diagnosis; infrared spectroscopy; nanotechnology; novel methods.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Akhtar S Shahzad K Mushtaq S Ali I Rafe MH Antibacterial and antiviral potential of colloidal Titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles suitable for biological applications. Materials Research Express. 2019;6:105409–105409.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
