Binary-QSAR guided virtual screening of FDA approved drugs and compounds in clinical investigation against SARS-CoV-2 main protease
- PMID: 34803447
- PMCID: PMC8573836
- DOI: 10.3906/biy-2106-61
Binary-QSAR guided virtual screening of FDA approved drugs and compounds in clinical investigation against SARS-CoV-2 main protease
Abstract
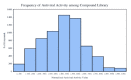
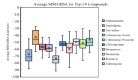
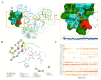
With the emergence of the new SARS-CoV-2 virus, drug repurposing studies have gained substantial importance. Combined with the efficacy of recent improvements in ligand- and target-based virtual screening approaches, virtual screening has become faster and more productive than ever. In the current study, an FDA library of approved drugs and compounds under clinical investigation were screened for their antiviral activity using the antiviral therapeutic activity binary QSAR model of the MetaCore/MetaDrug platform. Among 6733-compound collection, we found 370 compounds with a normalized therapeutic activity value greater than a cutoff of 0.75. Only these selected compounds were used for molecular docking studies against the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro). After initial short (10 ns) molecular dynamics (MD) simulations with the top-50 docking scored compounds and following molecular mechanics generalized born surface area (MM/GBSA) calculations, top-10 compounds were subjected to longer (100 ns) MD simulations and end-point MM/GBSA estimations. Our virtual screening protocol yielded Cefuroxime pivoxetil, an ester prodrug of second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic Cefuroxime, as being a considerable molecule for drug repurposing against the SARS-CoV-2 Mpro.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; drug repurposing; virtual screening; Binary QSAR.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors declare that there is not any conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Akhoon BA Tiwari H Nargotra A In silico drug design methods for drug repurposing. In Silico Drug Design. 2019:47–84.
-
- Dalerba P Levin B Thompson JL A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in. Covid-19. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2020;382 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
