Current Advancement on the Dynamic Mechanism of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
- PMID: 34803489
- PMCID: PMC8579455
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.65066
Current Advancement on the Dynamic Mechanism of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Abstract
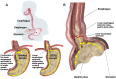
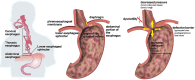
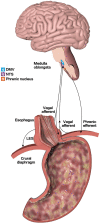
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common clinical disease associated with upper gastrointestinal motility disorders. Recently, with improvements in living standards and changes in lifestyle and dietary habits, the incidence of GERD has been increasing yearly. However, the mechanism of GERD has not been fully elucidated due to its complex pathogenesis, and this had led to unsatisfactory therapeutic outcomes. Currently, the occurrence and development of GERD involve multiple factors. Its pathogenesis is mainly thought to be related to factors, such as lower esophageal sphincter pressure, transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxation, crural diaphragmatic dysfunction, hiatus hernia, and impaired esophageal clearance. Therefore, explaining the pathogenesis of GERD more clearly and systematically, exploring potential and effective therapeutic targets, and choosing the best treatment methods have gradually become the focus of scholars' attention. Herein, we reviewed current advancements in the dynamic mechanism of GERD to better counsel patients on possible treatment options.
Keywords: advancement; anti-reflux barrier disruption; dynamic mechanism; esophageal clearance impaired; gastroesophageal reflux disease.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Maret-Ouda J, Markar SR, Lagergren J. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Review. JAMA. 2020;324:2536–47. - PubMed
-
- Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R, Global Consensus G. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101:1900–20. quiz 43. - PubMed
-
- Mehta RS, Staller K, Chan AT. Review of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. JAMA. 2021;325:1472. - PubMed
-
- Katzka DA, Kahrilas PJ. Advances in the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. BMJ. 2020;371:m3786. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

