MicroRNA-196a promotes renal cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting BRAM1 to regulate SMAD and MAPK signaling pathways
- PMID: 34803496
- PMCID: PMC8579441
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.60805
MicroRNA-196a promotes renal cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting BRAM1 to regulate SMAD and MAPK signaling pathways
Abstract
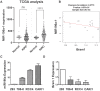
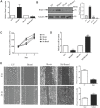
Rationale: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are endogenous ~22nt RNAs that play critical regulatory roles in various biological and pathological processes, including various cancers. Their function in renal cancer has not been fully elucidated. It has been reported that miR-196a can act as oncogenes or as tumor suppressors depending on their target genes. However, the molecular target for miR-196a and the underlying mechanism in miR-196a promoted cell migration and invasion in renal cancer is still not clear. Methods: The expression, survival and correlation between miR-196a and BRAM1 were investigated using TCGA analysis and validated by RT-PCR and western blot. To visualize the effect of Bram1 on tumor metastasis in vivo, NOD-SCID gamma (NSG) mice were intravenously injected with RCC4 cells (106 cells/mouse) or RCC4 overexpressing Bram1. In addition, cell proliferation assays, migration and invasion assays were performed to examine the role of miR-196a in renal cells in vitro. Furthermore, immunoprecipitation was done to explore the binding targets of Bram1. Results: TCGA gene expression data from renal clear cell carcinoma patients showed a lower level of Bram1 expression in patients' specimens compared to adjacent normal tissues. Moreover, Kaplan‑Meier survival data clearly show that high expression of Bram1correlates to poor prognosis in renal carcinoma patients. Our mouse metastasis model confirmed that Bram1 overexpression resulted in an inhibition in tumor metastasis. Target-prediction analysis and dual-luciferase reporter assay demonstrated that Bram1 is a direct target of miR-196a in renal cells. Further, our in vitro functional assays revealed that miR-196a promotes renal cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Rescue of Bram1 expression reversed miR-196a-induced cell migration. MiR-196a promotes renal cancer cell migration by directly targeting Bram1 and inhibits Smad1/5/8 phosphorylation and MAPK pathways through BMPR1A and EGFR. Conclusions: Our findings thus provide a new mechanism on the oncogenic role of miR-196a and the tumor-suppressive role of Bram1 in renal cancer cells. Dysregulated miR-196a and Bram1 represent potential prognostic biomarkers and may have therapeutic applications in renal cancer.
Keywords: Bram1; MicroRNA-196a; SMAD and MAPK pathways; migration and invasion; renal cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures







Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-196a promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion through targeting HOXA5.BMC Cancer. 2012 Aug 9;12:348. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-348. BMC Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22876840 Free PMC article.
-
miR-196a-5p promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer via targeting IκBα.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jan 8;19(1):30. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5245-1. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30621631 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen-induced miR-196a elevation promotes tumor growth and metastasis via targeting SPRED1 in breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2018 Apr 23;17(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0830-0. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29685157 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microRNA-196a in tumorigenesis, tumor progression, and prognosis.Tumour Biol. 2016 Dec;37:15457–15466. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5430-2. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27752997 Review.
-
The role and mechanism of action of microRNA-122 in cancer: Focusing on the liver.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Oct;123:110713. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110713. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37523968 Review.
Cited by
-
miRNAs as Interconnectors between Obesity and Cancer.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Apr 15;10(2):24. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10020024. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 38668382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
USP53 Affects the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Breast Cancer Cells by Regulating the Ubiquitination Level of ZMYND11.Biol Proced Online. 2024 Jul 23;26(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12575-024-00251-4. Biol Proced Online. 2024. PMID: 39044157 Free PMC article.
-
The m6A modification-mediated OGDHL exerts a tumor suppressor role in ccRCC by downregulating FASN to inhibit lipid synthesis and ERK signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Aug 25;14(8):560. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06090-7. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37626050 Free PMC article.
-
miR-378a-3p promotes renal cell carcinoma proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting TOB2.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Mar;25(3):748-757. doi: 10.1007/s12094-022-02984-8. Epub 2022 Oct 29. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36309620
-
The METTL3/miR-196a Axis Predicts Poor Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.J Cancer. 2024 Jan 21;15(6):1603-1612. doi: 10.7150/jca.92968. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38370374 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–54. - PubMed
-
- Lopez-Beltran A, Scarpelli M, Montironi R, Kirkali Z. 2004 WHO classification of the renal tumors of the adults. European urology. 2006;49:798–805. - PubMed
-
- Du M, Lu D, Wang Q, Chu H, Tong N, Pan X. et al. Genetic variations in microRNAs and the risk and survival of renal cell cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:1629–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

