Systematic Survey of the Alteration of the Faecal Microbiota in Rats With Gastrointestinal Disorder and Modulation by Multicomponent Drugs
- PMID: 34803663
- PMCID: PMC8596021
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.670335
Systematic Survey of the Alteration of the Faecal Microbiota in Rats With Gastrointestinal Disorder and Modulation by Multicomponent Drugs
Abstract
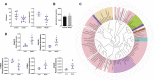
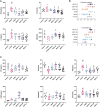
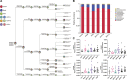
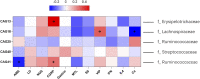
Gastrointestinal disorder (GID) is a global health disease which leads to heavy public medical burden. Disorders in the intestinal flora have been found in gastrointestinal disorder patients. However, the interaction between GID and the intestinal flora in faecal has not been studied comprehensively. In addition, multicomponent drugs represented by traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) are widely used for treating GID, but their modulation of the intestinal flora has not been investigated. Therefore, in this study, a high-throughput sequencing strategy was used to investigate alterations in the intestinal flora in a rat GID model, followed by an investigation of the modulation by a representative TCM, Xiaoerfupi (XEFP) granule. The results showed that in rats with GID, the relative abundances of Erysipelotrichaceae, Lachnospiraceae, Streptococcaceae increased and that of Ruminococcaceae decreased. At the macro level, the levels of LysoPC(16:0), LysoPC(20:2), LysoPC(15:0), LysoPC(20:2 (11Z, 14Z)), LysoPC(20:1), LysoPC(15:0), LysoPC(20:0) and LysoPE (0:0/20:0) in serum increased and levels of PC(36:4), PC(38:4), PC(o-36;4), PE (MonoMe(13,5)/MonoMe(11,5)) decreased. The imbalance of metabolites was restored by XEFP through ether lipid metabolism pathway. Increase in the phyla Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes (F/B) ratio of the GID rats was restored by XEFP as well. Moreover, XEFP can relief the symptoms of GID rats by increasing bacteria Ruminococcaceae and decreasing Streptococcaceae, Erysipelotrichaceae and Lachnospiraceae in faecal microbiota level. This study represents a comprehensive survey of the interaction between GID and the intestinal flora and a systematic evaluation of modulation by a multicomponent drug.
Keywords: XEFP; functional dyspepsia; intestinal flora; metabonomics; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2021 Wu, Wu, Wu, Wu, Ji, Xu, Zhang, Wei, Zhao and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

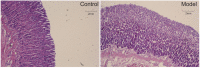
References
-
- Chen G., Feng P., Wang S., Ding X., Xiong J., Wu J., et al. (2020). An Herbal Formulation of Jiawei Xiaoyao for the Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia: A Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Clinical Trial. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 11, e00241. 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000241 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

