A Study Based on Metabolomics, Network Pharmacology, and Experimental Verification to Explore the Mechanism of Qinbaiqingfei Concentrated Pills in the treatment of Mycoplasma Pneumonia
- PMID: 34803705
- PMCID: PMC8599429
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.761883
A Study Based on Metabolomics, Network Pharmacology, and Experimental Verification to Explore the Mechanism of Qinbaiqingfei Concentrated Pills in the treatment of Mycoplasma Pneumonia
Abstract
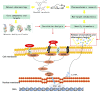
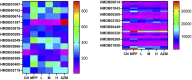
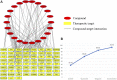
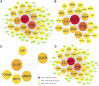
Qinbaiqingfei concentrated pills (QB) are a commonly used medicine for the treatment of mycoplasma pneumonia in China, and the mechanism of action of QB needs to be studied further. Therefore, we use a combination of metabolomics and network pharmacology to clarify the mechanism of QB. Nontarget metabolomics studies were performed on rat serum, urine, and lung tissues, and 56 therapeutic biomarkers were found. Subsequently, the components of QB absorbed into the blood and lung tissues were clarified, and based on this finding, the core target of network pharmacology was predicted. The enrichment analysis of biomarkers-genes finally confirmed their close relationship with the NF-κB signaling pathway. By western blotting expression of the proteins in the lung tissue-related signaling pathways, it is finally confirmed that QB inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway through SIRT1, IL-10 and MMP9, CTNNB1, EGFR, and other targets. It plays a role in regulating immunity, regulating metabolism, and treating diseases.
Keywords: NF-κB signaling pathway; Qinbaiqingfei concentrated pills; metabolomics; mycoplasma pneumonia; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Huo, Dong, Sun, Li, Zhang, Qin, pengna and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research study was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Exploring the mechanism of Qinbaiqingfei-concentrate pills in the treatment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia from the perspective of intestinal microbiota and mucosal immunity.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;293:115308. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115308. Epub 2022 Apr 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35460847
-
Revealing active ingredients, potential targets, and action mechanism of Ermiao fang for treating endometritis based on network pharmacology strategy.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Oct 5;260:113051. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113051. Epub 2020 Jun 4. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32505843
-
Network pharmacology combined with metabolomics to study the mechanism of Shenyan Kangfu Tablets in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 24;270:113817. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113817. Epub 2021 Jan 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33444720
-
5-Hydroxy-4-methoxycanthin-6-one alleviates dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in rats via regulation of metabolic profiling and suppression of NF-κB/p65 signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2021 Feb;82:153438. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153438. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33422953
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
RIPK1 and RIPK3 inhibitors: potential weapons against inflammation to treat diabetic complications.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 26;14:1274654. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1274654. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37954576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Zhixiao Tang on Anti-Inflammatory Multiple Targets and Multiple Components: Metabonomics Combined with Database Mining Technology.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 11;17:4587-4610. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S463067. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39011417 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology predicts targets and pathways of herbal components for the treatment of pneumonia: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2025 Jan 31;104(5):e41372. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000041372. Medicine (Baltimore). 2025. PMID: 39889188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Effects of Retinoic Acid in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction: Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Aug 30;15:4963-4979. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S358374. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36105385 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

