Quercetin Modulates IGF-I and IGF-II Levels After Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle-Damage: A Placebo-Controlled Study
- PMID: 34803913
- PMCID: PMC8595302
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2021.745959
Quercetin Modulates IGF-I and IGF-II Levels After Eccentric Exercise-Induced Muscle-Damage: A Placebo-Controlled Study
Abstract
Background: Prolonged or unaccustomed eccentric exercise may cause muscle damage and depending from its extent, this event negatively affects physical performance.
Objectives: The aim of the present investigation was to evaluate, in humans, the effect of the flavonoid quercetin on circulating levels of the anabolic insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-I) and insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF-II), produced during the recovery period after an eccentric-induced muscle damage (EIMD).
Methods: A randomized, double-blind, crossover study has been performed; twelve young men ingested quercetin (1 g/day) or placebo for 14 days and then underwent an eccentric-induced muscle damaging protocol. Blood samples were collected, and cell damage markers [creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and myoglobin (Mb)], the inflammatory responsive interleukin 6 (IL-6), IGF-I and IGF-II levels were evaluated before the exercise and at different recovery times from 24 hours to 7 days after EIMD.
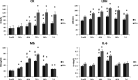
Results: We found that, in placebo treatment the increase in IGF-I (72 h) preceded IGF-II increase (7 d). After Q supplementation there was a more marked increase in IGF-I levels and notably, the IGF-II peak was found earlier, compared to placebo, at the same time of IGF-I (72 h). Quercetin significantly reduced plasma markers of cell damage [CK (p<0.005), LDH (p<0.001) and Mb (p<0.05)] and the interleukin 6 level [IL-6 (p<0.05)] during recovery period following EIMD compared to placebo.
Conclusions: Our data are encouraging about the use of quercetin as dietary supplementation strategy to adopt in order to mitigate and promote a faster recovery after eccentric exercise as suggested by the increase in plasma levels of the anabolic factors IGF-I and IGF-II.
Keywords: anabolic factors; anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; eccentric exercise; skeletal muscle mass recovery.
Copyright © 2021 Sgrò, Ceci, Lista, Patrizio, Sabatini, Felici, Sacchetti, Bazzucchi, Duranti and Di Luigi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

