MKK4 variants rs3826392 and rs3809728 are associated with susceptibility and clinicopathological features in colorectal cancer patients
- PMID: 34804420
- PMCID: PMC8591758
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2021.56874.12690
MKK4 variants rs3826392 and rs3809728 are associated with susceptibility and clinicopathological features in colorectal cancer patients
Abstract
Objectives: The mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 (MKK4) plays a key role in several processes like inflammation, apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. Several authors have proposed that genetic variations in these genes may alter their expression with subsequent cancer risk. This study aimed to examine the possible association of MKK4 rs3826392 and rs3809728 variants in Mexican patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). These variants were also compared with clinical features as sex, age, TNM stage, and tumor location.
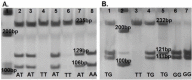
Materials and methods: The study included genomic DNA from 218 control subjects and 250 patients. Genotyping of the MKK4 variants was performed using polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) procedure.
Results: Individuals with A/T and T/T genotypes for the rs3809728 (-1044 A>T) variant showed a significantly increased risk for CRC (P=0.012 and 0.007, respectively); while individuals with the G/G genotype for the rs3826392 (-1304 T>G) variant showed a decreased risk for CRC (P=0.012). Genotypes of the MKK4 rs3809728 variant were also significantly related to colon localization and advanced TNM stage in CRC patients. T-T haplotype (rs3826392 and rs3809728) of the MKK4 gene was associated with risk in patients with CRC.
Conclusion: The rs3826392 variant in the MKK4 gene could be a cancer protective factor, while the rs3809728 variant could be a risk factor. These variants play a significant role in CRC risk.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Haplotypes; MKK4; Susceptibility; Variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association between -1304T>G polymorphism in the promoter of MKK4 gene and the risk of sporadic colorectal cancer in southern Chinese population.Int J Cancer. 2009 Oct 15;125(8):1876-83. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24575. Int J Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19610067
-
The association between -1304T>G polymorphism in the promoter of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 4 gene and the risk of cervical cancer in Chinese population.DNA Cell Biol. 2012 Jul;31(7):1167-73. doi: 10.1089/dna.2011.1586. Epub 2012 Feb 15. DNA Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22335172 Free PMC article.
-
Functional variant (-1304T>G) in the MKK4 promoter is associated with decreased risk of acute myeloid leukemia in a southern Chinese population.Cancer Sci. 2011 Aug;102(8):1462-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01965.x. Epub 2011 May 25. Cancer Sci. 2011. PMID: 21518142
-
RECK Variants are Associated with Clinicopathological Features and Decreased Susceptibility in Mexican Patients with Colorectal Cancer.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2022 Jun 8;257(2):163-169. doi: 10.1620/tjem.2022.J032. Epub 2022 Apr 21. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 35444107
-
A functional variant (-1304T>G) in the MKK4 promoter contributes to a decreased risk of lung cancer by increasing the promoter activity.Carcinogenesis. 2010 Aug;31(8):1405-11. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq126. Epub 2010 Jun 16. Carcinogenesis. 2010. PMID: 20554746
References
-
- Globocan. Colorectal cancer. 2020. URL: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/10_8_9-Colorectum-fact... [Accesed: April 15, 2021]
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Globocan. Mexico. 2020. URL: http://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/484-mexico-fact-she... [Accesed: April 15, 2021]
-
- Ocvirk S, Wilson AS, Appolonia CN, Thomas TK, O’Keefe SJD. Fiber, fat, and colorectal cancer: New insight into modifiable dietary risk factors. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019;21:62. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous