Transient Left Bundle Branch Block in the Setting of Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
- PMID: 34804750
- PMCID: PMC8592294
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.19568
Transient Left Bundle Branch Block in the Setting of Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema
Abstract
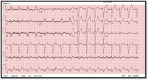
Cardiogenic pulmonary edema complicated by transient left bundle branch block (LBBB) is a relatively rare finding. We report a case of a 52-year-old woman with underlying heart failure but no structural heart disease who was referred for evaluation due to severe shortness of breath and documented LBBB on a 12-lead EKG. She was diagnosed with cardiogenic pulmonary edema due to medication noncompliance. With the resolution of her symptoms by treating her pulmonary edema with bisoprolol and furosemide, repeated EKG showed resolution of LBBB. A review of her medical records showed similar presentations of pulmonary edema associated with transient LBBB. In conclusion, to the best of our knowledge, transient LBBB associated with cardiogenic pulmonary edema is very uncommon. The etiology of transient LBBB remains unclear, however, the most likely theory that explains our patient's transient LBBB is a consequence of ventricular enlargement from fluid overload and cardiac muscle strain with dilatation, causing bundle conduction interruption. Our patient's cardiogenic pulmonary edema was complicated with transient LBBB in multiple previous presentations with a resolution of the LBBB after treating the underlying pulmonary edema.
Keywords: cardiogenic; intermittent; ischaemic heart disease; left bundle branch block; pulmonary edema; transient.
Copyright © 2021, Elgassim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transient Left Bundle Branch Block Induced Acute Heart Failure as a Consequence of Ramus Intermedius Occlusion.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2025 Jan;30(1):e70038. doi: 10.1111/anec.70038. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2025. PMID: 39645601 Free PMC article.
-
Transient left bundle branch block and intraventricular dyssynchrony as a cause of reversible left ventricular dysfunction: The "in vivo" documentation of spontaneous electrical remodeling.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019 Nov;24(6):e12667. doi: 10.1111/anec.12667. Epub 2019 May 29. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019. PMID: 31141243 Free PMC article.
-
Unmasking Coronary Artery Disease With Intermittent Left Bundle Branch Block: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Feb 13;16(2):e54155. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54155. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38496176 Free PMC article.
-
Episodic Left Bundle Branch Block-A Comprehensive Review of the Literature.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2016 Mar;21(2):117-25. doi: 10.1111/anec.12361. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2016. PMID: 27296905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemodynamic implications of left bundle branch block.J Electrocardiol. 2000;33 Suppl:115-21. doi: 10.1054/jelc.2000.20330. J Electrocardiol. 2000. PMID: 11265710 Review.
References
-
- Scherbak D, Hicks GJ. Treasure Island, Florida: StatPearls Publishing; 2021. Left Bundle Branch Block. - PubMed
-
- Transient left bundle branch block: an unusual electrocardiogram in acute pulmonary embolism. Kasmani R, Okoli K, Mohan G, Casey K, Ledrick D. Am J Med Sci. 2009;337:381–382. - PubMed
-
- Exercise-induced left bundle branch block during thallium 201 myocardial perfusion scintigraphy: a case report. Bozkurt MF, Yildirir A, Kabakçi G, Caner B. Angiology. 2001;52:145–148. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources