Seasonal Variation of Presentation of Perforated Peptic Ulcer Disease: An Overview of Patient Demographics, Management and Outcomes
- PMID: 34804752
- PMCID: PMC8597679
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.19618
Seasonal Variation of Presentation of Perforated Peptic Ulcer Disease: An Overview of Patient Demographics, Management and Outcomes
Abstract
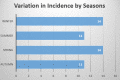
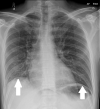
Background Perforated peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is one of the most common causes of acute peritonitis. It carries significant mortality and morbidity. Several previous studies have reported a seasonal variation in the presentation of patients with perforated ulcers. Here we present this study from our experience in a Northern Irish acute district hospital. Methods A retrospective cohort study was conducted on perforated peptic ulcer patients who presented to Altnagelvin Area Hospital emergency department between 2015 to 2020. Data on patient demographics, clinical presentation, investigations, management and outcomes were collected. Primary outcome was to investigate if seasonality was associated with the incidence of perforated peptic ulcers. Follow-up data were also collected. Seasons were defined as per UK Met Office. Results A total of 50 patients presented with perforated PUD. Male to female ratio was approximately 3:2. Peaks were noted in spring and winter. April was the most common month for presentation followed by December. Smoking was the most common risk factor followed by alcohol abuse. Fourteen patients (28%) were either very frail or had contained perforations and were conservatively managed. Three deaths were noted (6%). Thirteen patients (26%) required ICU admission at some stage in their management. Conclusion Slight seasonal variation was noted in the presentation of perforated peptic ulcers in our study with a higher incidence in the winter and spring months. The month of April was noted to have the peak incidence of the disease in our study.
Keywords: free air under the diaphragm; gastric perforation; intestinal perforation; perforated duodenal ulcer; perforated peptic ulcer.
Copyright © 2021, Yawar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Malik TF, Gnanapandithan K, Singh K. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls; 202130521213. Peptic Ulcer Disease. - PubMed
-
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and dyspepsia in adults: investigation and management [CG 184] https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg184 2014 - PubMed
-
- Peptic ulcer disease. Lanas A, Chan FKL. Lancet. 2017;390:613–624. - PubMed
-
- Surgical approach and prognostic factors after peptic ulcer perforation. Hermansson M, Staël von Holstein C, Zilling T. Eur J Surg. 1999;165:566–572. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
