Smart healthcare IoT applications based on fog computing: architecture, applications and challenges
- PMID: 34804767
- PMCID: PMC8595960
- DOI: 10.1007/s40747-021-00582-9
Smart healthcare IoT applications based on fog computing: architecture, applications and challenges
Abstract
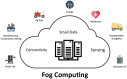
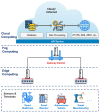
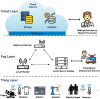
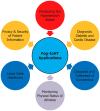
The history of human development has proven that medical and healthcare applications for humanity always are the main driving force behind the development of science and technology. The advent of Cloud technology for the first time allows providing systems infrastructure as a service, platform as a service and software as a service. Cloud technology has dominated healthcare information systems for decades now. However, one limitation of cloud-based applications is the high service response time. In some emergency scenarios, the control and monitoring of patient status, decision-making with related resources are limited such as hospital, ambulance, doctor, medical conditions in seconds and has a direct impact on the life of patients. To solve these challenges, optimal computing technologies have been proposed such as cloud computing, edge computing, and fog computing technologies. In this article, we make a comparison between computing technologies. Then, we present a common architectural framework based on fog computing for Internet of Health Things (Fog-IoHT) applications. Besides, we also indicate possible applications and challenges in integrating fog computing into IoT Healthcare applications. The analysis results indicated that there is huge potential for IoHT applications based on fog computing. We hope, this study will be an important guide for the future development of fog-based Healthcare IoT applications.
Keywords: Cloud computing; Fog computing; Healthcare; Internet of Things.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Qadri YA, Nauman A, Zikria YB, Vasilakos AV, Kim SW. The future of healthcare internet of things: a survey of emerging technologies. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor. 2020;22(2):1121–1167. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2020.2973314. - DOI
-
- Buke A, Gaoli F, Yongcai W, Lei S, Zhiqi Y. Healthcare algorithms by wearable inertial sensors: a survey. China Commun. 2015;12(4):1–12. doi: 10.1109/CC.2015.7114054. - DOI
-
- Kumar A, Krishnamurthi R, Nayyar A, Sharma K, Grover V, Hossain E. A novel smart healthcare design, simulation, and implementation using healthcare 4.0 processes. IEEE Access. 2020;8:118433–118471. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3004790. - DOI
-
- Zhang R, Xue R, Liu L. Searchable encryption for healthcare clouds: a survey. IEEE Trans Serv Comput. 2018;11(6):978–996. doi: 10.1109/TSC.2017.2762296. - DOI
-
- Fan K, Zhu S, Zhang K, Li H, Yang Y. A lightweight authentication scheme for cloud-based RFID healthcare systems. IEEE Netw. 2019;33(2):44–49. doi: 10.1109/MNET.2019.1800225. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources