Transthoracic Vector Flow Imaging in Pediatric Patients with Valvular Stenosis - A Proof of Concept Study
- PMID: 34804771
- PMCID: PMC8598391
- DOI: 10.1055/a-1652-1261
Transthoracic Vector Flow Imaging in Pediatric Patients with Valvular Stenosis - A Proof of Concept Study
Abstract
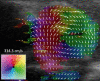
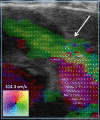
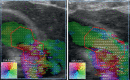
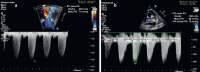
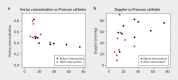
Purpose Continuous wave Doppler ultrasound is routinely used to detect cardiac valve stenoses. Vector flow imaging (VFI) is an angle-independent real-time ultrasound method that can quantify flow complexity. We aimed to evaluate if quantification of flow complexity could reliably assess valvular stenosis in pediatric patients. Materials and Methods Nine pediatric patients with echocardiographically confirmed valvular stenosis were included in the study. VFI and Doppler measurements were compared with transvalvular peak-to-peak pressure differences derived from invasive endovascular catheterization. Results Vector concentration correlated with the catheter measurements before intervention after exclusion of one outlier (r=-0.83, p=0.01), whereas the Doppler method did not (r=0.49, p=0.22). The change in vector concentration after intervention correlated strongly with the change in the measured catheter pressure difference (r=-0.86, p=0.003), while Doppler showed a tendency for a moderate correlation (r=0.63, p=0.07). Conclusion Transthoracic flow complexity quantification calculated from VFI data is feasible and may be useful for assessing valvular stenosis severity in pediatric patients.
Keywords: catheters; echocardiography; vector flow imaging, valvular stenosis, pressure gradient.
The Author(s). This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial-License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Ramin Moshavegh is employed at BK Medical Aps. Jørgen Arendt Jensen developed and patented the vector flow imaging technique.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Accuracy of the Doppler-derived pressure gradient in pediatric patients with aortic valvular stenosis: is the correction for pressure recovery necessary?Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi. 2010 Jul;85(4):225-31. Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 20718206
-
Quantification of pressure gradients across stenotic valves by Doppler ultrasound.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983 Oct;2(4):707-18. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(83)80311-8. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983. PMID: 6886232
-
Quantification of transvalvular pressure differences in aortic stenosis by Doppler ultrasound.Int J Cardiol. 1985 Feb;7(2):121-8. doi: 10.1016/0167-5273(85)90350-x. Int J Cardiol. 1985. PMID: 3156098
-
Cardiac catheterization and other imaging modalities in the evaluation of valvular heart disease.Curr Opin Cardiol. 1993 Mar;8(2):211-5. doi: 10.1097/00001573-199303000-00004. Curr Opin Cardiol. 1993. PMID: 10148391 Review.
-
Assessment of valvular heart disease with Doppler echocardiography.JAMA. 1989 Oct 20;262(15):2131-5. JAMA. 1989. PMID: 2677426 Review.
References
-
- Yoganathan A P, Cape E G, Sung H W. Review of hydrodynamic principles for the cardiologist: applications to the study of blood flow and jets by imaging techniques. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1988;12:1344–1353. - PubMed
-
- Ringle A, Castel A-L, Le Goffic C. Prospective assessment of the frequency of low gradient severe aortic stenosis with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction: Critical impact of aortic flow misalignment and pressure recovery phenomenon. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;111:518–527. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2017.11.004. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

