Successful management of Aspergillus infection of an open window thoracostomy with topical liposomal amphotericin B
- PMID: 34804785
- PMCID: PMC8581452
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mmcr.2021.08.004
Successful management of Aspergillus infection of an open window thoracostomy with topical liposomal amphotericin B
Abstract
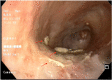
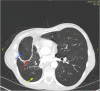
We present the case of a previously healthy 54-year-old man who was hospitalized for an Aspergillus fumigatus infection of an open window thoracotomy. Patient was successfully treated for 8 consecutives weeks with daily topical pleural liposomal amphotericine B administered by soaked gauzes combined with systemic therapy.
Keywords: Aspergillus; Empyema; Open window thoracotomy; Pleural antifungal therapy.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of International Society for Human and Animal Mycology.
Conflict of interest statement
There are none.
Figures

References
-
- Meredith H., Cogan B., McLauglin B. Pleural aspergillosis Am.J Roentgeol. 1978;130:164–166. - PubMed
-
- Almuhareb A., Habib Z. Management of Aspergillus pleural empyema with combined systemic and intrapleural antifungal therapy in a pediatric patient: case report. J Infect Public Health. 2018 Mar-Apr;11(2):280–282. - PubMed
-
- Bonatti H., Lass-Floerl C., Angerer K., Singh N., Lechner M., Stelzmueller I., Singh R., Schmid T., Geltner C. Successful management of postpneumonectomy Aspergillus pleural empyema by combined surgical and anti-fungal treatment with voriconazole and caspofungin. Mycoses. 2010;53(5):448–454. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

