Protective effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on rat retinal neurons in hyperglycemia through the brain-derived neurotrophic factor/TrkB pathway
- PMID: 34804857
- PMCID: PMC8569562
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2021.11.06
Protective effect of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on rat retinal neurons in hyperglycemia through the brain-derived neurotrophic factor/TrkB pathway
Abstract
Aim: To explore whether human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (hUCMSC)-derived exosomes (hUCMSC-Exos) protect rat retinal neurons in high-glucose (HG) conditions by activating the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-TrkB pathway.
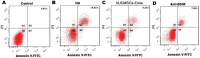
Methods: hUCMSC-Exos were collected with differential ultracentrifugation methods and observed by transmission electron microscopy. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) was used to quantify BDNF in hUCMSC-Exos, and Western blot was used to identify surface markers of hUCMSC-Exos. Rat retinal neurons were divided into 4 groups. Furthermore, cell viability, cell apoptosis, and TrkB protein expression were measured in retinal neurons.
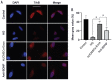
Results: hUCMSCs and isolated hUCMSC-Exos were successfully cultured. All hUCMSC-Exos showed a diameter of 30 to 150 nm and had a phospholipid bimolecular membrane structure, as observed by transmission electron microscopy. ELISA showed the BDNF concentration of hUCMSCs-Exos was 2483.16±281.75. hUCMSCs-Exos effectively reduced the apoptosis of retinal neuron rate and improved neuron survival rate, meanwhile, the results of immunofluorescence verified the fluorescence intensity of TrKB in neurons increased. And all above effects were reduced by treated hUCMSCs-Exos with BDNF inhibitors. hUCMSC-Exos effectively reduced the apoptosis rate of retinal neurons by activating the BDNF-TrkB pathway in a HG environment.
Conclusion: In the HG environment, hUCMSC-Exos could carry BDNF into rat retinal neurons, inhibiting neuronal apoptosis by activating the BDNF-TrkB pathway.
Keywords: BDNF-TrkB pathway; diabetic retinopathy; exosomes; human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells; retinal neurons.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures


References
-
- Xu Y, Wang L, He J, et al. 2010 China Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance Group. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 2013;310(9):948–959. - PubMed
-
- Abbaszadeh H, Ghorbani F, Derakhshani M, Movassaghpour AA, Yousefi M, Talebi M, Shamsasenjan K. Regenerative potential of Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells: a new horizon of stem cell therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(12):9230–9240. - PubMed
-
- Drela K, Lech W, Figiel-Dabrowska A, Zychowicz M, Mikula M, Sarnowska A, Domanska-Janik K. Enhanced neuro-therapeutic potential of Wharton's Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in comparison with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells culture. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(4):497–509. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
