The effects of propolis supplementation on metabolic parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials
- PMID: 34804893
- PMCID: PMC8588957
- DOI: 10.22038/AJP.2021.18046
The effects of propolis supplementation on metabolic parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials
Abstract
Objective: Propolis is a sticky, resinous substance produced by honeybees from various plants. Various biological properties of propolis and its extracts have been recognized in previous studies including the antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antiviral, hepatoprotective, antitumor, antibacterial and antimycotic properties. This study aimed to summarize the effect of propolis on metabolic parameters in human adults using systematic review and meta-analysis.
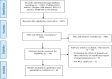
Materials and methods: A comprehensive systematic search was performed in ISI Web of Science, PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar up to July 2020 for controlled clinical trials evaluating the impact of propolis on lipid profile and liver enzyme biomarkers. A random effects model was used to calculate the weighted mean difference (WMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) as the difference between the mean for the intervention and control groups.
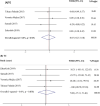
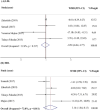
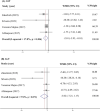
Results: The present meta-analysis included six randomized controlled trials. There was significant reduction in Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) in comparison to the control groups (WMD=-2.01; 95% CI: -3.93--0.10; p=0.039). However, a non-significant effect was observed in Triglycerides (TG), Total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), High-density lipoprotein (HDL) (WMD=-0.05 mg/dl; 95% CI: -0.27-0.18; p=0.688; WMD=7.08 mg/dl; 95% CI: -37.31-51.46; p=0.755; WMD=-0.94 mg/dl; 95% CI: -6.64-4.77; p=0.747; WMD=3.14 mg/dl; 95% CI: -1.84-8.13; p=0.216, respectively).
Conclusion: Current meta-analysis revealed that propolis supplementation can reduce AST; nevertheless, there was no significant effect on lipid profile indices and ALT.
Keywords: Lipid profile; Liver enzyme; Metabolic parameter; Propolis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of carnitine supplementation on clinical characteristics of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Med. 2020 Jan;48:102273. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.102273. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Complement Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 31987257
-
The effects of probiotic supplementation and exercise training on liver enzymes and cardiometabolic markers in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2024 Aug 1;21(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12986-024-00826-8. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2024. PMID: 39090657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of propolis on anthropometric indices and lipid profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020 Aug 12;19(2):1835-1843. doi: 10.1007/s40200-020-00604-2. eCollection 2020 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020. PMID: 33520864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The beneficial effects of cinnamon among patients with metabolic diseases: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022;62(22):6113-6131. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.1896473. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2022. PMID: 33739219
-
The effects of resveratrol on lipid profiles and liver enzymes in patients with metabolic syndrome and related disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Feb 17;19(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-1198-x. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32066446 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Potential Effects of Bioactive Compounds of Plant-Based Foods and Medicinal Plants in Chronic Kidney Disease and Dialysis: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2024 Dec 14;16(24):4321. doi: 10.3390/nu16244321. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39770942 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Propolis and Chitosan Nanoparticles against Ibuprofen-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Albino Rats.Diseases. 2024 Feb 29;12(3):49. doi: 10.3390/diseases12030049. Diseases. 2024. PMID: 38534974 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanolic Extract Propolis-Loaded Niosomes Diminish Phospholipase B1, Biofilm Formation, and Intracellular Replication of Cryptococcus neoformans in Macrophages.Molecules. 2023 Aug 24;28(17):6224. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176224. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687052 Free PMC article.
-
The Honey Bee Apis mellifera: An Insect at the Interface between Human and Ecosystem Health.Biology (Basel). 2022 Feb 1;11(2):233. doi: 10.3390/biology11020233. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Propolis Consumption on Liver Enzymes and Obesity Indices in Adults: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis.Curr Dev Nutr. 2024 Aug 13;8(9):104438. doi: 10.1016/j.cdnut.2024.104438. eCollection 2024 Sep. Curr Dev Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39296926 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afsharpour F, Hashemipour S, Khadem-haghighian H, Koushan Y. Effects of Iranian propolis on glycemic status, inflammatory factors, and liver enzyme levels in type 2 diabetic patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial. J Nutr Sci Diet. 2017:9–14.
-
- Afsharpour F, Javadi M, Hashemipour S, Koushan Y. Propolis supplementation improves glycemic and antioxidant status in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Complement Ther Med. 2019;43:283–288. - PubMed
-
- Attia YA, Al-Hamid AA, Ibrahim MS, Al-Harthi M, Bovera F, Elnaggar AS. Productive performance, biochemical and hematological traits of broiler chickens supplemented with propolis, bee pollen, and mannan oligosaccharides continuously or intermittently. Livest Sci. 2014;164:87–95.
-
- Azab E, Algridi MA, Lashkham NM. Hypolipidemic and antiatherogenic effects of aqueous extract of Libyan propolis in lead acetate intoxicated male albino mice. IJSR. 2015;4:1060–1068.
-
- Bankova VS, de Castro SL, Marcucci MC. Propolis: recent advances in chemistry and plant origin. Apidologie. 2000;31:3–15.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
