RBM8A Promotes Glioblastoma Growth and Invasion Through the Notch/STAT3 Pathway
- PMID: 34804926
- PMCID: PMC8600138
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.736941
RBM8A Promotes Glioblastoma Growth and Invasion Through the Notch/STAT3 Pathway
Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma (GBM) is a prevalent brain malignancy with an extremely poor prognosis, which is attributable to its invasive biological behavior. The RNA-binding motif protein 8A (RBM8A) has different effects on various human cancers. However, the role of RBM8A in GBM progression remains unclear.
Methods: We investigated the expression levels of RBM8A in 94 GBM patients and explored the correlation between RBM8A expression and patient prognosis. Using in vitro and in vivo assays, combined with GBM sequencing data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) and the Chinese Glioma Genome Atlas (CGGA), we examined whether and how RBM8A contributes to GBM progression.
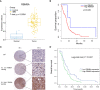
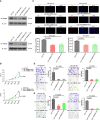
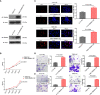
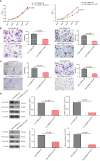
Results: RBM8A was up-regulated in GBM tissues, and its higher expression correlated with worse prognosis. Knockdown of RBM8A inhibited GBM progression and invasion ability both in vitro and in vivo. On the contrary, overexpression of RBM8A promoted GBM progression and invasion ability. Enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes in GBM data identified the Notch1/STAT3 network as a potential downstream target of RBM8A, and this was supported by molecular docking studies. Furthermore, we demonstrated that RBM8A regulates the transcriptional activity of CBF1. The γ-secretase inhibitor DAPT significantly reversed RBM8A-enhanced GBM cell proliferation and invasion, and was associated with down-regulation of p-STAT3 and Notch1 protein. Finally, the gene set variance analysis score of genes involved in regulation of the Notch1/STAT3 network by RBM8A showed good diagnostic and prognostic value for GBM.
Conclusions: RBM8A may promote GBM cell proliferation and migration by activating the Notch/STAT3 pathway in GBM cells, suggesting that RBM8A may serve as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of GBM.
Keywords: Notch; RBM8A; glioblastoma; prognosis; stat3.
Copyright © 2021 Lin, Wei, Hu, Zhang, Wei, Qian and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 4 A-3 promotes glioblastoma growth and invasion through the Notch1-dependent pathway.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 15;23(1):550. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10946-8. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37322413 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insights and Prognosis Associated With RBM8A in Glioblastoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Apr 29;9:876603. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.876603. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35573726 Free PMC article.
-
Chromobox 7/8 serve as independent indicators for glioblastoma via promoting proliferation and invasion of glioma cells.Front Neurol. 2022 Aug 11;13:912039. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.912039. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36034290 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling Pathways Regulating the Expression of the Glioblastoma Invasion Factor TENM1.Biomedicines. 2022 May 10;10(5):1104. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051104. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of STAT3 in the pathogenesis and treatment of glioblastoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Feb 27;11:1098482. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1098482. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36923251 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Diverse Roles of the Exon Junction Complex Factors in the Cell Cycle, Cancer, and Neurodevelopmental Disorders-Potential for Therapeutic Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 8;23(18):10375. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810375. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Candidate Genes Associated With Prognosis in Glioblastoma.Front Mol Neurosci. 2022 Jul 7;15:913328. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.913328. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35875673 Free PMC article.
-
RBM8A, a new target of TEAD4, promotes breast cancer progression by regulating IGF1R and IRS-2.J Transl Med. 2024 Sep 4;22(1):823. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05639-0. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39232805 Free PMC article.
-
Rbm8a regulates neurogenesis and reduces Alzheimer's disease-associated pathology in the dentate gyrus of 5×FAD mice.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Apr;19(4):863-871. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.382254. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 37843222 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Cell Infiltration into the Brain in Glioblastoma: From Mechanisms to Clinical Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 17;14(2):443. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020443. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053605 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Butowski NA, Chang SM. Glial Tumors: The Current State of Scientific Knowledge. Clin Neurosurg (2006) 53:106–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

