Clinicopathological and Preclinical Patient-Derived Model Studies Define High Expression of NRN1 as a Diagnostic and Therapeutic Target for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 34804954
- PMCID: PMC8595331
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.758503
Clinicopathological and Preclinical Patient-Derived Model Studies Define High Expression of NRN1 as a Diagnostic and Therapeutic Target for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Acquired therapeutic resistance and metastasis/recurrence remain significant challenge in advance renal cell carcinoma (RCC), thus the establishment of patient-derived cancer models may provide a clue to assess the problem. We recently characterized that neuritogenesis-related protein neuritin 1 (NRN1) functions as an oncogene in testicular germ cell tumor. This study aims to elucidate the role of NRN1 in RCC.
Methods: NRN1 expression in clinical RCC specimens was analyzed based on immunohistochemistry. NRN1-associated genes in RCC were screened by the RNA-sequencing dataset from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). RCC patient-derived cancer cell (RCC-PDC) spheroid cultures were established and their viabilities were evaluated under the condition of gene silencing/overexpression. The therapeutic effect of NRN1-specific siRNA was evaluated in RCC-PDC xenograft models.
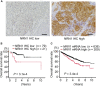
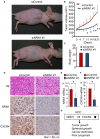
Results: NRN1 immunoreactivity was positively associated with shorter overall survival in RCC patients. In TCGA RCC RNA-sequencing dataset, C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4), a prognostic and stemness-related factor in RCC, is a gene whose expression is substantially correlated with NRN1 expression. Gain- and loss-of-function studies in RCC-PDC spheroid cultures revealed that NRN1 significantly promotes cell viability along with the upregulation of CXCR4. The NRN1-specific siRNA injection significantly suppressed the proliferation of RCC-PDC-derived xenograft tumors, in which CXCR4 expression is significantly repressed.
Conclusion: NRN1 can be a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target in RCC as analyzed by preclinical patient-derived cancer models and clinicopathological studies.
Keywords: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; cancer stem-like cell; cancer stemness; neuritin 1; patient-derived cancer cell (PDC); patient-derived xenograft; renal cell carcinoma; spheroid.
Copyright © 2021 Kamada, Ikeda, Suzuki, Sato, Kitayama, Kawakami, Ichikawa, Horie and Inoue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial of financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
HIF1α inhibitor 2-methoxyestradiol decreases NRN1 expression and represses in vivo and in vitro growth of patient-derived testicular germ cell tumor spheroids.Cancer Lett. 2020 Oct 1;489:79-86. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.05.040. Epub 2020 Jun 13. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32544513
-
DCLK1 is a broadly dysregulated target against epithelial-mesenchymal transition, focal adhesion, and stemness in clear cell renal carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 10;6(4):2193-205. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3059. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25605241 Free PMC article.
-
Neuritin 1 expression in human normal tissues and its association with various human cancers.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Apr 1;11(4):1956-1964. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31938301 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of CXCR4 high expression in renal cell carcinoma: A meta-analysis and literature review.Int J Surg. 2019 Nov;71:12-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.08.021. Epub 2019 Sep 5. Int J Surg. 2019. PMID: 31494331
-
Choosing The Right Animal Model for Renal Cancer Research.Transl Oncol. 2020 Mar;13(3):100745. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2020.100745. Epub 2020 Feb 22. Transl Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32092671 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment and Functional Characterization of Murine Monoclonal Antibodies Recognizing Neuritin.Antibodies (Basel). 2023 Apr 7;12(2):28. doi: 10.3390/antib12020028. Antibodies (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37092449 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

