ARID1A Mutation in Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Potential Therapeutic Target
- PMID: 34804958
- PMCID: PMC8599951
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.759577
ARID1A Mutation in Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Potential Therapeutic Target
Abstract
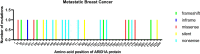
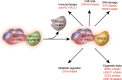
Distant metastasis is the principal cause of mortality for breast cancer patients. Targeting specific mutations that have been acquired during the evolution process of advanced breast cancer is a potential means of enhancing the clinical efficacy of treatment strategies. In metastatic breast cancer, ARID1A is the most prevalent mutation of the SWI/SNF complex, which regulates DNA repair, recombination, and gene transcription. The low expression of ARID1A is associated with poor disease-free survival and overall survival of patients with luminal A or HER2-rich breast cancer. In addition, ARID1A plays a prominent role in maintaining luminal characteristics and has an advantage for identifying responses to treatment, including endocrine therapies, HDAC inhibitors and CDK4/6 inhibitors. The therapeutic vulnerabilities initiated by ARID1A alterations encourage us to explore new approaches to cope with ARID1A mutant-related drug resistance or metastasis. In this review, we describe the mutation profiles of ARID1A in metastatic breast cancer and the structure and function of ARID1A and the SWI/SNF complex as well as discuss the potential mechanisms of ARID1A-mediated endocrine resistance and therapeutic potential.
Keywords: ARID1A; SWI/SNF complex; endocrine resistance; metastatic breast cancer; synthetic lethality; therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2021 Cheng, Zhao, Dong and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ARID1A determines luminal identity and therapeutic response in estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer.Nat Genet. 2020 Feb;52(2):198-207. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0554-0. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Nat Genet. 2020. PMID: 31932695 Free PMC article.
-
ARID1A mutant ovarian clear cell carcinoma: A clear target for synthetic lethal strategies.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018 Dec;1870(2):176-184. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.07.005. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30025943 Review.
-
Loss of the SWI/SNF-ATPase subunit members SMARCF1 (ARID1A), SMARCA2 (BRM), SMARCA4 (BRG1) and SMARCB1 (INI1) in oesophageal adenocarcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jan 6;20(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6425-3. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31906887 Free PMC article.
-
Treating ARID1A mutated cancers by harnessing synthetic lethality and DNA damage response.J Biomed Sci. 2022 Sep 19;29(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12929-022-00856-5. J Biomed Sci. 2022. PMID: 36123603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SWI/SNF Alterations in Squamous Bladder Cancers.Genes (Basel). 2020 Nov 19;11(11):1368. doi: 10.3390/genes11111368. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33227989 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pathogenic variant profile in DNA damage response genes correlates with metastatic breast cancer progression-free survival in a Mexican-mestizo population.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 27;13:1146008. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1146008. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37182128 Free PMC article.
-
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in androgen receptor-positive triple-negative breast cancer: potential predictive biomarkers and genetic alterations.Breast Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 20;27(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13058-025-01994-y. Breast Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 40114215 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic targeting of ARID1A-deficient cancer cells with RITA (Reactivating p53 and inducing tumor apoptosis).Cell Death Dis. 2024 May 29;15(5):375. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06751-1. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38811536 Free PMC article.
-
Coexistent ARID1A-PIK3CA mutations are associated with immune-related pathways in luminal breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 27;13(1):20911. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-48002-x. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 38017109 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms behind context-dependent role of glucocorticoids in breast cancer progression.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022 Dec;41(4):803-832. doi: 10.1007/s10555-022-10047-1. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022. PMID: 35761157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Cancer Day 2021: Spotlight on IARC Research Related to Breast Cancer. Available at: https://www.iarc.who.int/featured-news/world-cancer-day-2021/.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

