Pulsatilla chinensis Saponins Ameliorate Inflammation and DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats by Regulating the Composition and Diversity of Intestinal Flora
- PMID: 34804990
- PMCID: PMC8602866
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.728929
Pulsatilla chinensis Saponins Ameliorate Inflammation and DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rats by Regulating the Composition and Diversity of Intestinal Flora
Abstract
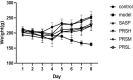
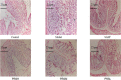
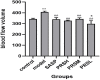
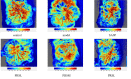
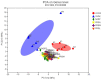
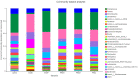
Pulsatilla chinensis (Bunge) Regel is a commonly used Chinese medicine for clearing away heat and detoxification, cooling blood, stopping dysentery, and anti-inflammatory effects. Pulsatilla chinensis saponins (PRS) have been identified to be responsible for producing these pharmacological activities. Studies have shown that Pulsatilla decoction has a good therapeutic effect on ulcerative colitis (UC), however, the therapeutic effect of PRS on UC has not been reported. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to investigate the possible anti-UC activity of PRS using a dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced rat model, and further study the mechanism of PRS in the treatment of UC. The fecal and colon samples were collected from rats to monitor the changes in the composition and diversity of the intestinal flora, and pathological colon sections were also made to examine the mesenteric hemorheological characteristics. The results showed that PRS significantly reduced the mesenteric blood flow in UC rats and significantly alleviated the inflammatory response, which indicates that saponins are involved in the anti-UC effects of PRS. At the same time, it is also suggested that the regulation of intestinal flora by Pulsatilla chinensis saponins is an important pathway for its anti-UC activity, which may be ascribed to the increase in beneficial bacteria like norank_F_Muribaculaceae and norank_F_norank_O_Clostridia_UCG-014, and decrease in the harmful Bacteroides.
Keywords: 16S rRNA; Pulsatilla chinensis saponins (PRS); dextran sulfate sodium (DSS); gut microbiome; ulcerative colitis (UC).
Copyright © 2021 Liu, Zhou, Yang, Jin, Song, Chen, Gao, Ai and Su.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Pulsatilla chinensis saponins improve SCFAs regulating GPR43-NLRP3 signaling pathway in the treatment of ulcerative colitis.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 May 23;308:116215. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116215. Epub 2023 Feb 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36806339
-
Pulsatilla decoction improves DSS-induced colitis via modulation of fecal-bacteria-related short-chain fatty acids and intestinal barrier integrity.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jan 10;300:115741. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115741. Epub 2022 Sep 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36162543
-
Anemone chinensis Bunge aqueous enema alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via inhibition of inflammation and regulation of the colonic mucosal microbiota.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Apr 24;288:114916. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114916. Epub 2022 Jan 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34998930
-
Therapeutic potential of triterpenoid saponin anemoside B4 from Pulsatilla chinensis.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Oct;160:105079. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105079. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32679180 Review.
-
Changes in serum inflammatory cytokine levels and intestinal flora in a self-healing dextran sodium sulfate-induced ulcerative colitis murine model.Life Sci. 2020 Dec 15;263:118587. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118587. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 33065145 Review.
Cited by
-
Pulsatillae radix extract alleviates DSS-induced colitis via modulating gut microbiota and inflammatory signaling pathway in mice.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 2;9(11):e21869. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21869. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38034600 Free PMC article.
-
Liupao tea aqueous extract alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in rats by modulating the gut microbiota.Open Life Sci. 2025 May 20;20(1):20251106. doi: 10.1515/biol-2025-1106. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40417008 Free PMC article.
-
Alginate Oligosaccharide Alleviates Salmonella Typhimurium-Induced Liver Injury by Regulating Oxidative Stress, Apoptosis, and Inflammatory Signaling Pathway.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Aug 15. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10650-y. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 40815366
-
Gut microbiota as predictors of the occurrence of high on-treatment platelet reactivity in acute ischemic stroke patients.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jan 4;13:1257317. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1257317. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38239505 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Herbal Therapy on Intestinal Microbiota and Serum Metabolomics in Different Rat Models of Mongolian Medicine.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 30;2022:7255780. doi: 10.1155/2022/7255780. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35677380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bloemendaal F. M., Becker M., Koelink P. J., Van D., Bemelman W. A., D’Haens G. R. A. M., et al. . (2020). Dop82 Macrophages in Crohn’s Disease Mesentery Are Predominantly Inflammatory and Produce Calprotectin. J. Crohns Colitis. 14, 121–122. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjz203.121 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

