Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption by Lipopolysaccharide and Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy
- PMID: 34804998
- PMCID: PMC8599158
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.768108
Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption by Lipopolysaccharide and Sepsis-Associated Encephalopathy
Abstract
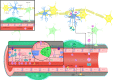
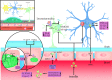
As a complex multicellular structure of the vascular system at the central nervous system (CNS), the blood-brain barrier (BBB) separates the CNS from the system circulation and regulates the influx and efflux of substances to maintain the steady-state environment of the CNS. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the cell wall component of Gram-negative bacteria, can damage the barrier function of BBB and further promote the occurrence and development of sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE). Here, we conduct a literature review of the direct and indirect damage mechanisms of LPS to BBB and the relationship between these processes and SAE. We believe that after LPS destroys BBB, a large number of inflammatory factors and neurotoxins will enter and damage the brain tissue, which will activate brain immune cells to mediate inflammatory response and in turn further destroys BBB. This vicious circle will ultimately lead to the progression of SAE. Finally, we present a succinct overview of the treatment of SAE by restoring the BBB barrier function and summarize novel opportunities in controlling the progression of SAE by targeting the BBB.
Keywords: blood-brain barrier; central nervous system; inflammation; lipopolysaccharide; oxidative stress; sepsis-associated encephalopathy.
Copyright © 2021 Peng, Luo, He, Zhang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Poldip2 mediates blood-brain barrier disruption in a model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy.J Neuroinflammation. 2019 Nov 28;16(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1575-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2019. PMID: 31779628 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting blood-brain barrier for sepsis-associated encephalopathy: Regulation of immune cells and ncRNAs.Brain Res Bull. 2024 Apr;209:110922. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.110922. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Brain Res Bull. 2024. PMID: 38458135 Review.
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction mediated through dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) propagates impairment in blood brain barrier in septic encephalopathy.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Jan 27;17(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1689-8. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 31987040 Free PMC article.
-
[Research progress on the changes of blood-brain barrier in sepsis-associated encephalopathy].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024 Aug;36(8):892-896. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20231109-00959. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2024. PMID: 39238417 Review. Chinese.
-
Mast cell activation mediates blood-brain barrier impairment and cognitive dysfunction in septic mice in a histamine-dependent pathway.Front Immunol. 2023 Feb 1;14:1090288. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1090288. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36817492 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Intersecting Pathways: The Role of Metabolic Dysregulation, Gastrointestinal Microbiome, and Inflammation in Acute Ischemic Stroke Pathogenesis and Outcomes.J Clin Med. 2024 Jul 21;13(14):4258. doi: 10.3390/jcm13144258. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39064298 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated encephalopathy.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 22;10(12):e33458. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33458. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39027435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disrupted metabolic and spontaneous neuronal activity of hippocampus in sepsis associated encephalopathy rats: A study combining magnetic resonance spectroscopy and resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging.Front Neurosci. 2022 Nov 17;16:1032098. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1032098. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36466179 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Blood-Brain Barrier Protection by Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids.Cells. 2023 Feb 18;12(4):657. doi: 10.3390/cells12040657. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Relationships between microbiome and neurodegeneration].Nervenarzt. 2023 Oct;94(10):885-891. doi: 10.1007/s00115-023-01537-w. Epub 2023 Sep 6. Nervenarzt. 2023. PMID: 37672084 Review. German.
References
-
- Alexandrov P. N., Hill J. M., Zhao Y., Bond T., Taylor C. M., Percy M. E., et al. . (2020). Aluminum-Induced Generation of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) From the Human Gastrointestinal (GI)-Tract Microbiome-Resident Bacteroides Fragilis. J. Inorg Biochem. 203, 110886. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.110886 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

