Targeting Mechanosensitive Piezo1 Alleviated Renal Fibrosis Through p38MAPK-YAP Pathway
- PMID: 34805150
- PMCID: PMC8602364
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.741060
Targeting Mechanosensitive Piezo1 Alleviated Renal Fibrosis Through p38MAPK-YAP Pathway
Abstract
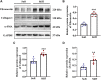
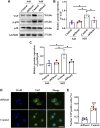
Renal fibrosis is the most common pathological manifestation of a wide variety of chronic kidney disease. Increased extracellular matrix (ECM) secretion and enhanced microenvironment stiffening aggravate the progression of renal fibrosis. However, the related mechanisms remain unclear. Here, we evaluated the mechanism by which ECM stiffness aggravates renal fibrosis. In the present study, renal mesangial cells (MCs) were cultured on polyacrylamide hydrogels with different stiffness accurately detected by atomic force microscope (AFM), simulating the in vivo growth microenvironment of MCs in normal kidney and renal fibrosis. A series of in vitro knockdown and activation experiments were performed to establish the signaling pathway responsible for mechanics-induced MCs activation. In addition, an animal model of renal fibrosis was established in mice induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO). Lentiviral particles containing short hairpin RNA (sh RNA) targeting Piezo1 were used to explore the effect of Piezo1 knockdown on matrix stiffness-induced MCs activation and UUO-induced renal fibrosis. An in vitro experiment demonstrated that elevated ECM stiffness triggered the activation of Piezo1, which increased YAP nuclear translocation through the p38MAPK, and consequently led to increased ECM secretion. Furthermore, these consequences have been verified in the animal model of renal fibrosis induced by UUO and Piezo1 knockdown could alleviate UUO-induced fibrosis and improve renal function in vivo. Collectively, our results for the first time demonstrate enhanced matrix stiffness aggravates the progression of renal fibrosis through the Piezo1-p38MAPK-YAP pathway. Targeting mechanosensitive Piezo1 might be a potential therapeutic strategy for delaying the progression of renal fibrosis.
Keywords: Piezo1; YAP; extracellular matrix secreation; matrix stiffness; renal fibrosis.
Copyright © 2021 Fu, Wan, Zhang, Li, Xing, Zou, Wang, Peng, Zhu, Cao and Zhai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Mechanosensitive Cation Channel Piezo1 Is Involved in Renal Fibrosis Induction.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 31;25(3):1718. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031718. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PIEZO1 mediates matrix stiffness-induced tumor progression in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma by activating the Ca2+/Calpain/YAP pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2025 Jan;1872(1):119871. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2024.119871. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2025. PMID: 39490703
-
Mechanosensitive Piezo1 channels mediate renal fibrosis.JCI Insight. 2022 Apr 8;7(7):e152330. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.152330. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35230979 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanical stiffness promotes skin fibrosis via Piezo1-Wnt2/Wnt11-CCL24 positive feedback loop.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jan 24;15(1):84. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06466-3. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38267432 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Mechanotransduction at the Transcriptional Level: YAP and BRD4 Are Novel Therapeutic Targets for the Reversal of Liver Fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2016 Dec 1;7:462. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00462. eCollection 2016. Front Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27990121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fibrosis: cross-organ biology and pathways to development of innovative drugs.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025 Jul;24(7):543-569. doi: 10.1038/s41573-025-01158-9. Epub 2025 Mar 18. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2025. PMID: 40102636 Review.
-
Activation of Piezo1 by intracranial hypertension induced neuronal apoptosis via activating hippo pathway.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Sep;30(9):e14872. doi: 10.1111/cns.14872. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39328029 Free PMC article.
-
Piezo2 expression and its alteration by mechanical forces in mouse mesangial cells and renin-producing cells.Sci Rep. 2022 Mar 10;12(1):4197. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07987-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35273307 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanosensitive Cation Channel Piezo1 Is Involved in Renal Fibrosis Induction.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 31;25(3):1718. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031718. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piezo1-Mediated Mechanotransduction Contributes to Disturbed Flow-Induced Atherosclerotic Endothelial Inflammation.J Am Heart Assoc. 2024 Nov 5;13(21):e035558. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.123.035558. Epub 2024 Oct 25. J Am Heart Assoc. 2024. PMID: 39450718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blythe N. M., Muraki K., Ludlow M. J., Stylianidis V., Gilbert H. T. J., Evans E. L., et al. (2019). Mechanically Activated Piezo1 Channels of Cardiac Fibroblasts Stimulate P38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Activity and Interleukin-6 Secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 294 (46), 17395–17408. 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009167 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bugg D., Bretherton R., Kim P., Olszewski E., Nagle A., Schumacher A. E., et al. (2020). Infarct Collagen Topography Regulates Fibroblast Fate via P38-Yes-Associated Protein Transcriptional Enhanced Associate Domain Signals. Circ. Res. 127 (10), 1306–1322. 10.1161/circresaha.119.316162 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

