Reenvisioning Traditional to Regenerative Therapeutic Advances in Managing Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 34805412
- PMCID: PMC8601846
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/7692447
Reenvisioning Traditional to Regenerative Therapeutic Advances in Managing Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
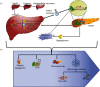
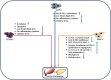
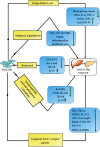
Reports indicate the increasing prevalence of liver disorders in diabetes mellitus (DM) patients. Clinically, it has also been revealed that the existence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) enhances the incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), while T2DM exacerbates NAFLD to extremely severe forms of steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. This implies the coexistence and bidirectional nature of NAFLD and T2DM, which function synergistically to drive adverse consequences in clinical practice. For treatment of such comorbid state, though the existing practices such as lifestyle management, traditional Chinese medicines (TCM), and pharmaceuticals have offered somewhat relief, the debate continues about the optimal therapeutic impacts. Recent developments in the field of tissue engineering have led to a renewed interest in novel biomaterial alternatives such as stem cells. This might be attributable to their differentiation potential towards hepatic and pancreatic lineage. These cellular therapies could be further complemented by platelet-derived biomaterials, TCM formulations, or any specific drug. Based on these abovementioned approaches, we aimed to comprehensively analyze various preclinical and clinical studies from traditional to regenerative therapeutic approaches in managing concomitant NAFLD and T2DM.
Copyright © 2021 Lung-Wen Tsai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; New Kids on the Block.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(2):172-181. doi: 10.2174/1570161117666190405164313. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 30961499 Review.
-
The Intricate Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM), Insulin Resistance (IR), and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD).J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jul 31;2020:3920196. doi: 10.1155/2020/3920196. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32832560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanism of Fufang Zhenzhu Tiaozhi capsule in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease based on network pharmacology and validation in minipigs.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Jun 28;274:114056. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114056. Epub 2021 Mar 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33771638
-
Concurrent nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes: diagnostic and therapeutic considerations.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019 Sep;13(9):849-866. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2019.1649981. Epub 2019 Aug 8. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31353974 Review.
-
Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes: Part II: Treatment.Diabetes Metab J. 2019 Apr;43(2):127-143. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2019.0034. Diabetes Metab J. 2019. PMID: 30993937 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ciardullo S., Monti T., Perseghin G. High prevalence of advanced liver fibrosis assessed by transient elastography among U.S. adults with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care . 2021;44(2):519–525. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

