Duck Interleukin-22: Identification and Expression Analysis in Riemerella anatipestifer Infection
- PMID: 34805416
- PMCID: PMC8601822
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3862492
Duck Interleukin-22: Identification and Expression Analysis in Riemerella anatipestifer Infection
Abstract
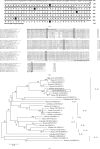
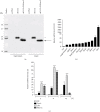
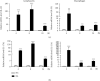
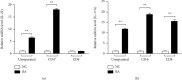
Riemerella anatipestifer is one of the most devastating pathogens affecting the global duck farms. Infection is involved in secretion of proinflammatory cytokines, including interleukin- (IL-) 17A. During the immune response to infection, IL-22 and IL-17A are often produced concurrently and at high levels in inflamed tissues. Little is known about duck IL-22 (duIL-22) during R. anatipestifer infection. We describe the characterization of duIL-22 and its mRNA expression analysis in splenic lymphocytes and macrophages treated with heat-killed R. anatipestifer and in the spleens and livers of R. anatipestifer-infected ducks. Full-length cDNA of duIL-22 encoded 197 amino acids. The deduced amino acid sequence of duIL-22 shared a 30.4-40.5% similarity with piscine counterparts, 57.4-60.1% with mammalian homologs, and 93.4% similarity to the chicken. Duck IL-22 mRNA expression level was relatively high in the skin of normal ducks. It was increased in mitogen-stimulated splenic lymphocytes and in killed R. anatipestifer-activated splenic lymphocytes and macrophages. Compared with healthy ducks, IL-22 transcript expression was significantly upregulated in the livers and spleens on days 1 and 4 postinfection, but not on day 7. IL-17A was significantly increased in the spleens only on day 4 postinfection and in the livers at all time points. When splenic lymphocytes were stimulated with heat-killed R. anatipestifer, CD4+ cells predominantly produced IL-22 while IL-17A was expressed both by CD4+ and CD4- cells. These results suggested that IL-22 and IL-17A are likely expressed in different cell types during R. anatipestifer infection.
Copyright © 2021 Rochelle A. Flores et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identification of duck IL-4 and its inhibitory effect on IL-17A expression in R. anatipestifer-stimulated splenic lymphocytes.Mol Immunol. 2018 Mar;95:20-29. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29407573
-
Riemerella anatipestifer infection in ducks induces IL-17A production, but not IL-23p19.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 13;9(1):13269. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49516-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31519917 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and expression analysis of duck interleukin-17D in Riemerella anatipestifer infection.Dev Comp Immunol. 2016 Aug;61:190-7. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Dev Comp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27060655
-
Upregulation of duck interleukin-17A during Riemerella anatipestifer infection.Dev Comp Immunol. 2016 Oct;63:36-46. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2016.05.009. Epub 2016 May 17. Dev Comp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27212414
-
Downregulation of common cytokine receptor γ chain inhibits inflammatory responses in macrophages stimulated with Riemerella anatipestifer.Dev Comp Immunol. 2018 Apr;81:225-234. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2017.12.009. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Dev Comp Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29241952
Cited by
-
Promotion of Th1 and Th2 responses over Th17 in Riemerella anatipestifer stimulation in chicken splenocytes: Correlation of gga-miR-456-3p and gga-miR-16-5p with NOS2 and CCL5 expression.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 6;18(11):e0294031. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294031. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37930983 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-22 facilitates the interferon-λ-mediated production of tripartite motif protein 25 to inhibit replication of duck viral hepatitis A virus type 1.Vet Res. 2023 Jun 30;54(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s13567-023-01188-4. Vet Res. 2023. PMID: 37391858 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Analysis and Immune Response of YaeT Protein Against Riemerella anatipestifer in Ducks.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Dec;195(12):7483-7501. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04445-6. Epub 2023 Apr 1. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37004647 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

