Enhancing polyp detection: technological advances in colonoscopy imaging
- PMID: 34805583
- PMCID: PMC8573375
- DOI: 10.21037/tgh.2020.02.05
Enhancing polyp detection: technological advances in colonoscopy imaging
Abstract
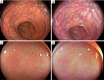
The detection and removal of polyps at colonoscopy is core to the current colorectal cancer (CRC) prevention strategy. However, colonoscopy is flawed with a well described miss rate and variability in detection rates associated with incomplete protection from CRC. Consequently, there is significant interest in techniques and technologies which increase polyp detection with the aim to remedy colonoscopy's ills. Technologic advances in colonoscope imaging are numerous and include; increased definition of imaging, widening field of view, virtual technologies to supplant conventional chromocolonoscopy (CC) and now computer assisted detection. However, despite nearly two decades of technologic advances, data on gains in detection from individual technologies have been modest at best and heterogenous and conflicted as a rule. This state of detection technology science is exacerbated by use of relatively blunt metrics of improvement without consensus, the myopic search for gains over single generations of technology improvement and an unhealthy focus on adenomatous lesions. Yet there remains cause for optimism as detection gains from new technology, while small, may still improve CRC prevention. The technologies are also readily available in current generation colonoscopes and have roles beyond simply detection such as lesion characterization, further improving their worth. Coupled with the imminent expansion of computer assisted detection the detection future from colonoscope imaging advances looks bright. This review aims to cover the major imaging advances and evidence for improvement in polyp detection.
Keywords: AI; Colonoscopy; advances; detection; high definition (HD); imaging; polyp; virtual chromoendoscopy.
2021 Translational Gastroenterology and Hepatology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
