Effect Modification of Body Mass Index and Kidney Function on Insulin Sensitivity Among Patients With Moderate CKD and Healthy Controls
- PMID: 34805633
- PMCID: PMC8589704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.08.031
Effect Modification of Body Mass Index and Kidney Function on Insulin Sensitivity Among Patients With Moderate CKD and Healthy Controls
Abstract
Introduction: Insulin resistance and obesity are prevalent in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. The interaction of body mass index (BMI) and kidney function across the continuum of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) is unknown.
Methods: In a cross-sectional study of 139 patients, 52 with CKD stages 3 and 4 and 87 patients with normal eGFR, we measured the insulin sensitivity index (ISI) using the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). We investigated the interaction between eGFR and BMI in their association with ISI and HOMA-IR using linear models with robust standard errors.
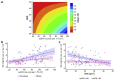
Results: Median age was 56 (42, 66) years, 50.4% were female, and 36% were African American. Patients with low eGFR (∼30 ml/min per 1.73 m2) had low ISI (2.3 mg/min per μU/ml) regardless of BMI. Among patients with preserved eGFR (>90 ml/min per 1.73m2), BMI had a greater effect on ISI (6.3 mg/min per μU/ml at a BMI of 20 kg/m2 vs. 4.6 mg/min per μU/ml at a BMI of 30 kg/m2) (P for interaction = 0.046). In models adjusted for demographics, and log transformed interleukin-6, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, leptin, and adiponectin, a 1-SD (28 ml/min per 1.73 m2) lower eGFR was associated with a statistically significant 1.14-unit decrease in ISI (95% confidence interval = -1.80, -0.48) among nonobese patients. Among obese patients, the effect estimate was -0.25 (95% confidence interval = -0.88, 0.39). The association between BMI and HOMA-IR was stronger in patients with lower eGFR (P for interaction = 0.005).
Conclusion: Both eGFR and BMI are independently associated with insulin sensitivity, but the strength of the association between BMI and insulin sensitivity varies significantly across eGFR.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; insulin resistance; interaction; kidney function; obesity.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Peripheral Insulin Resistance Is Associated with Copeptin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease.Kidney360. 2021 Jul 8;2(9):1434-1440. doi: 10.34067/KID.0002622021. eCollection 2021 Sep 30. Kidney360. 2021. PMID: 35373107 Free PMC article.
-
Hematologic malignancies magnify the effect of body mass index on insulin resistance in cancer survivors.Blood Adv. 2022 Apr 12;6(7):1981-1990. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006241. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 35130338 Free PMC article.
-
Correlates of insulin resistance in older individuals with and without kidney disease.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011 Sep;26(9):2814-9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfq817. Epub 2011 Jan 19. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011. PMID: 21248294 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Anthropometric and Biochemical Determinants of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate in a Large Cohort of Obese Children.J Ren Nutr. 2018 Sep;28(5):359-362. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2018.01.001. Epub 2018 Feb 13. J Ren Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29452889
-
Plasma adiponectin concentration has an inverse and a non linear association with estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with K/DOQI 3 - 5 chronic kidney disease.Clin Nephrol. 2009 Jul;72(1):21-30. doi: 10.5414/cnp72021. Clin Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19640384 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Mediterranean diet as a strategy for preserving kidney function in patients with coronary heart disease with type 2 diabetes and obesity: a secondary analysis of CORDIOPREV randomized controlled trial.Nutr Diabetes. 2024 May 16;14(1):27. doi: 10.1038/s41387-024-00285-3. Nutr Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38755195 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Research hotspots and future trends in lipid metabolism in chronic kidney disease: a bibliometric and visualization analysis from 2004 to 2023.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Sep 3;15:1401939. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1401939. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39290864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith D., DeFronzo R.A. Insulin resistance in uremia mediated by postbinding defects. Kidney Int. 1982;22:54–62. - PubMed
-
- Hung A., Pupim L., Yu C., et al. Determinants of C-reactive protein in chronic hemodialysis patients: relevance of dialysis catheter utilization. Hemodialysis Int. 2008;12:236–243. - PubMed
-
- Hung A.M., Ikizler T.A. Factors determining insulin resistance in chronic hemodialysis patients. Contrib Nephrol. 2011;171:127–134. - PubMed
-
- Trirogoff M.L., Shintani A., Himmelfarb J., et al. Body mass index and fat mass are the primary correlates of insulin resistance in nondiabetic stage 3–4 chronic kidney disease patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86:1642–1648. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

