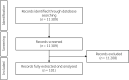
A rapid evidence assessment exploring whether antimicrobial resistance complicates non-infectious health conditions and healthcare services, 2010-20
- PMID: 34806009
- PMCID: PMC8599069
- DOI: 10.1093/jacamr/dlab171
A rapid evidence assessment exploring whether antimicrobial resistance complicates non-infectious health conditions and healthcare services, 2010-20
Abstract
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the greatest public health threats at this time. While there is a good understanding of the impacts of AMR on infectious diseases, an area of less focus is the effects AMR may be having on non-communicable health conditions (such as cancer) and healthcare services (such as surgery). Therefore, this study aimed to explore what impact AMR is currently having on non-communicable health conditions, or areas of health services, where AMR could be a complicating factor impacting on the ability to treat the condition and/or health outcomes. To do this, a rapid evidence assessment of the literature was conducted, involving a systematic approach to searching and reviewing the evidence. In total, 101 studies were reviewed covering surgery, organ transplants, cancer, ICUs, diabetes, paediatric patients, immunodeficiency conditions, liver and kidney disease, and physical trauma. The results showed limited research in this area and studies often use a selective population, making the results difficult to generalize. However, the evidence showed that for all health conditions and healthcare service areas reviewed, at least one study demonstrated a higher risk of death for patients with resistant infections, compared with no or drug-susceptible infections. Poor health outcomes were also associated with resistant infections in some instances, such as severe sepsis and failure of treatments, as well as a greater need for invasive medical support. While there are gaps in the evidence base requiring further research, efforts are also needed within policy and practice to better understand and overcome these challenges.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The future of Cochrane Neonatal.Early Hum Dev. 2020 Nov;150:105191. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2020.105191. Epub 2020 Sep 12. Early Hum Dev. 2020. PMID: 33036834
-
Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data.Epidemiol Prev. 2017 Sep-Dec;41(5-6 (Suppl 2)):1-128. doi: 10.19191/EP17.5-6S2.P001.100. Epidemiol Prev. 2017. PMID: 29205995 English, Italian.
-
Beyond the black stump: rapid reviews of health research issues affecting regional, rural and remote Australia.Med J Aust. 2020 Dec;213 Suppl 11:S3-S32.e1. doi: 10.5694/mja2.50881. Med J Aust. 2020. PMID: 33314144
-
Population-level mathematical modeling of antimicrobial resistance: a systematic review.BMC Med. 2019 Apr 24;17(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12916-019-1314-9. BMC Med. 2019. PMID: 31014341 Free PMC article.
-
Global geographic trends in antimicrobial resistance: the role of international travel.J Travel Med. 2019 Dec 23;26(8):taz036. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taz036. J Travel Med. 2019. PMID: 31115466 Review.
Cited by
-
Mortality risks associated with empirical antibiotic activity in Escherichia coli bacteraemia: an analysis of electronic health records.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022 Aug 25;77(9):2536-2545. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkac189. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35723965 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Biological Properties of Whey Peptides and Their Role as Emerging Therapeutics in Immune Tolerance.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 7;17(6):938. doi: 10.3390/nu17060938. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40289962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Silico Docking, Resistance Modulation and Biofilm Gene Expression in Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii via Cinnamic and Gallic Acids.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jun 28;11(7):870. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11070870. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884124 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Neill J. Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. 2014. https://www.jpiamr.eu/app/uploads/2014/12/AMR-Review-Paper-Tackling-a-cr....
-
- WHO. Antimicrobial Resistance. https://www.who.int/health-topics/antimicrobial-resistance.
-
- ECDC. Factsheet for the General Public - Antimicrobial Resistance. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/antimicrobial-resistance/facts/factsheets/....
-
- ReAct. World Health Day – the Rise and Fall of Antibiotics? 2018. https://www.reactgroup.org/news-and-views/news-and-opinions/year-2018/wo....
-
- CDC. Leading Causes of Death, 1900-1998. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/dvs/lead1900_98.pdf.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources