Common Fundamentals of Psoriasis and Depression
- PMID: 34806760
- PMCID: PMC9455336
- DOI: 10.2340/actadv.v101.565
Common Fundamentals of Psoriasis and Depression
Abstract
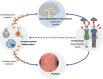
Psoriasis is an inflammatory, immune-mediated disease that is frequently associated with psychological comorbidities such as depression. The stigma patients feel because of the appearance of their skin may contribute to the high psycho-social burden of psoriasis. However, there is emerging evidence that overlapping biological mechanisms are, to a substantial degree, responsible for the close interaction between psoriasis and depression. Increased proinflammatory mediators, such as C-reactive protein or interleukin-6, are present in both psoriasis and depression, indicating that inflammation may represent a pathophysiological link between the diseases. Anti-inflammatory biologic therapies treat the clinical manifestations of psoriasis, but might also play a significant role in reducing associated depressive symptoms in patients with psoriasis. Comparison between single studies focusing on the change in depressive symptoms in psoriasis is limited by inconsistency in the depression screening tools applied.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Schafer I, Rustenbach SJ, Radtke M, Augustin J, Glaeske G, Augustin M. Epidemiologie der Psoriasis in Deutschland – Auswertung von Sekundärdaten einer gesetzlichen Krankenversicherung. Gesundheitswesen 2011; 73: 308–313. - PubMed
-
- Tribo MJ, Turroja M, Castano-Vinyals G, Bulbena A, Ros E, Garcia-Martinez P, et al. . Patients with moderate to severe psoriasis associate with higher risk of depression and anxiety symptoms: results of a multivariate study of 300 Spanish individuals with psoriasis. Acta Derm Venereol 2019; 99: 417–422. - PubMed
-
- Lamb RC, Matcham F, Turner MA, Rayner L, Simpson A, Hotopf M, et al. . Screening for anxiety and depression in people with psoriasis: a cross-sectional study in a tertiary referral setting. Br J Dermatol 2017; 176: 1028–1034. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

