Extracellular Matrix in Heart Failure: Role of ADAMTS5 in Proteoglycan Remodeling
- PMID: 34806902
- PMCID: PMC8687617
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055732
Extracellular Matrix in Heart Failure: Role of ADAMTS5 in Proteoglycan Remodeling
Abstract
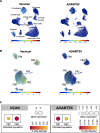
Background: Remodeling of the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a hallmark of heart failure (HF). Our previous analysis of the secretome of murine cardiac fibroblasts returned ADAMTS5 (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5) as one of the most abundant proteases. ADAMTS5 cleaves chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans such as versican. The contribution of ADAMTS5 and its substrate versican to HF is unknown.
Methods: Versican remodeling was assessed in mice lacking the catalytic domain of ADAMTS5 (Adamts5ΔCat). Proteomics was applied to study ECM remodeling in left ventricular samples from patients with HF, with a particular focus on the effects of common medications used for the treatment of HF.
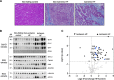
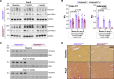
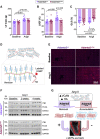
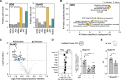
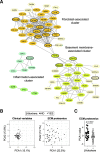
Results: Versican and versikine, an ADAMTS-specific versican cleavage product, accumulated in patients with ischemic HF. Versikine was also elevated in a porcine model of cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury and in murine hearts after angiotensin II infusion. In Adamts5ΔCat mice, angiotensin II infusion resulted in an aggravated versican build-up and hyaluronic acid disarrangement, accompanied by reduced levels of integrin β1, filamin A, and connexin 43. Echocardiographic assessment of Adamts5ΔCat mice revealed a reduced ejection fraction and an impaired global longitudinal strain on angiotensin II infusion. Cardiac hypertrophy and collagen deposition were similar to littermate controls. In a proteomics analysis of a larger cohort of cardiac explants from patients with ischemic HF (n=65), the use of β-blockers was associated with a reduction in ECM deposition, with versican being among the most pronounced changes. Subsequent experiments in cardiac fibroblasts confirmed that β1-adrenergic receptor stimulation increased versican expression. Despite similar clinical characteristics, patients with HF treated with β-blockers had a distinct cardiac ECM profile.
Conclusions: Our results in animal models and patients suggest that ADAMTS proteases are critical for versican degradation in the heart and that versican accumulation is associated with impaired cardiac function. A comprehensive characterization of the cardiac ECM in patients with ischemic HF revealed that β-blockers may have a previously unrecognized beneficial effect on cardiac chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan content.
Keywords: adrenergic beta-agonists; extracellular matrix; heart failure; proteoglycans.
Figures

References
-
- Baudino TA, Carver W, Giles W, Borg TK. Cardiac fibroblasts: friend or foe? Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2006; 291:H1015–H1026. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00023.2006 - PubMed
-
- Rienks M, Papageorgiou AP, Frangogiannis NG, Heymans S. Myocardial extracellular matrix: an ever-changing and diverse entity. Circ Res. 2014; 114:872–888. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302533 - PubMed
-
- Reilly MP, Li M, He J, Ferguson JF, Stylianou IM, Mehta NN, Burnett MS, Devaney JM, Knouff CW, Thompson JR, et al. ; Myocardial Infarction Genetics Consortium; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Identification of ADAMTS7 as a novel locus for coronary atherosclerosis and association of ABO with myocardial infarction in the presence of coronary atherosclerosis: two genome-wide association studies. Lancet. 2011; 377:383–392. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61996-4 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prins BP, Mead TJ, Brody JA, Sveinbjornsson G, Ntalla I, Bihlmeyer NA, van den Berg M, Bork-Jensen J, Cappellani S, Van Duijvenboden S, et al. Exome-chip meta-analysis identifies novel loci associated with cardiac conduction, including ADAMTS6. Genome Biol. 2018; 19:87. doi: 10.1186/s13059-018-1457-6 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

