Stereotactic radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases: dose-size response relationship in the era of immunotherapy
- PMID: 34807342
- PMCID: PMC8606626
- DOI: 10.1007/s11060-021-03899-0
Stereotactic radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases: dose-size response relationship in the era of immunotherapy
Abstract
Purpose/objective(s): To determine, for intact melanoma brain metastases (MBM) treated with single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS), whether planning parameter peripheral dose per lesion diameter (PDLDm, Gy/mm) and lesion control (LC) differs with versus without immunotherapy (IO).
Materials/methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of patients with intact MBM treated with SRS from 2008 to 2019. Cox-frailty models were constructed to include confounders selected by penalized Cox regression models with a LASSO selector. Interaction effect testing was used to determine whether a significant effect between IO and PDLDm could be demonstrated with respect to LC.
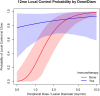
Results: The study cohort comprised 67 patients with 244 MBMs treated with SRS (30 patients with 122 lesions treated with both SRS and IO) were included. The logarithm of PDLDm was selected as a predictor of LC (HR 0.307, 95% CI 0.098-0.441), adjusting for IO receipt (HR 0.363, 95% CI 0.108-1.224). Interaction effect testing demonstrated a differential effect of PDLDm by IO receipt, with respect to LC (p = 0.048). Twelve-month LC rates for a 7.5 mm lesion receiving SRS (18 Gy) with IO versus without IO were 87.8% (95% CI 69.0-98.3%) versus 79.8% (95% CI 55.1-93.8%) respectively.
Conclusion: PDLDm predicted LC in patients with small MBMs treated with single-fraction SRS. We found a differential effect of dose per lesion size and LC by immunotherapy receipt. Future studies are needed to determine whether lower doses of single-fraction SRS afford similarly effective LC for patients with small MBMs receiving immunotherapy.
Keywords: Brain metastasis; Dose; Immunotherapy; Melanoma; Size; Stereotactic radiosurgery.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Yusuf MB, Amsbaugh MJ, Burton E, Chesney J, Woo S. Peri-SRS administration of immune checkpoint therapy for melanoma metastatic to the brain: investigating efficacy and the effects of relative treatment timing on lesion response. World Neurosurg. 2017;100:632–640.e634. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2017.01.101. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

