Poly(acrylamide- co- N, N'-methylenebisacrylamide) Monoliths for High-Peak-Capacity Hydrophilic-Interaction Chromatography-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry of Intact Proteins at Low Trifluoroacetic Acid Content
- PMID: 34807576
- PMCID: PMC8655738
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.1c03473
Poly(acrylamide- co- N, N'-methylenebisacrylamide) Monoliths for High-Peak-Capacity Hydrophilic-Interaction Chromatography-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry of Intact Proteins at Low Trifluoroacetic Acid Content
Abstract
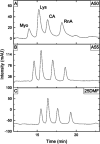
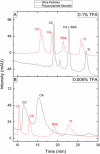
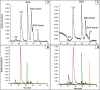
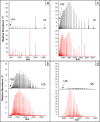
In this study, we optimized a polymerization mixture to synthesize poly(acrylamide-co-N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide) monolithic stationary phases for hydrophilic-interaction chromatography (HILIC) of intact proteins. Thermal polymerization was performed, and the effects of varying the amount of cross-linker and the porogen composition on the separation performance of the resulting columns were studied. The homogeneity of the structure and the different porosities were examined through scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Further characterization of the monolithic structure revealed a permeable (Kf between 2.5 × 10-15 and 1.40 × 10-13 m2) and polar stationary phase suitable for HILIC. The HILIC separation performance of the different columns was assessed using gradient separation of a sample containing four intact proteins, with the best performing stationary phase exhibiting a peak capacity of 51 in a gradient of 25 min. Polyacrylamide-based materials were compared with a silica-based particulate amide phase (2.7 μm core-shell particles). The monolith has no residual silanol sites and, therefore, fewer sites for ion-exchange interactions with proteins. Thus, it required lower concentrations of ion-pair reagent in HILIC of intact proteins. When using 0.1% of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), the peak capacities of the two columns were similar (30 and 34 for the monolithic and packed column, respectively). However, when decreasing the concentration of TFA to 0.005%, the monolithic column maintained similar separation performance and selectivity (peak capacity 23), whereas the packed column showed greatly reduced performance (peak capacity 12), lower selectivity, and inability to elute all four reference proteins. Finally, using a mobile phase containing 0.1% formic acid and 0.005% TFA, the HILIC separation on the monolithic column was successfully hyphenated with high-resolution mass spectrometry. Detection sensitivity for protein and glycoproteins was increased and the amount of adducts formed was decreased in comparison with separations performed at 0.1% TFA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effect of charged groups on hydrophilic monolithic stationary phases on their chromatographic properties.J Chromatogr A. 2016 Oct 21;1469:77-87. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2016.09.059. Epub 2016 Sep 25. J Chromatogr A. 2016. PMID: 27692647
-
Influence of ion-pairing reagents on the separation of intact glycoproteins using hydrophilic-interaction liquid chromatography - high-resolution mass spectrometry.J Chromatogr A. 2023 Jan 11;1688:463721. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463721. Epub 2022 Dec 15. J Chromatogr A. 2023. PMID: 36565654
-
Preparation and evaluation of 400μm I.D. polymer-based hydrophilic interaction chromatography monolithic columns with high column efficiency.J Chromatogr A. 2017 Aug 4;1509:83-90. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2017.06.034. Epub 2017 Jun 14. J Chromatogr A. 2017. PMID: 28629939
-
[Development of hydrophilic interaction chromatographic hyphenated techniques and their applications].Se Pu. 2008 Nov;26(6):649-57. Se Pu. 2008. PMID: 19253538 Review. Chinese.
-
Trends in monoliths: Packings, stationary phases and nanoparticles.J Chromatogr A. 2023 Feb 22;1691:463819. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2023.463819. Epub 2023 Jan 25. J Chromatogr A. 2023. PMID: 36724721 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrophilic Interaction Chromatography HRMS with Acrylamide Monolithic Columns: A Novel Approach for Intact Antibody Glycoform Characterization.Anal Chem. 2025 Jul 1;97(25):13569-13576. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c02033. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40518936 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoflow Size Exclusion Chromatography-Native Mass Spectrometry of Intact Proteoforms and Protein Complexes.Anal Chem. 2025 Jun 17;97(23):12241-12250. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5c01019. Epub 2025 Jun 6. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40476594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wouters B.; Dapic I.; Valkenburg T. S. E.; Wouters S.; Niezen L.; Eeltink S.; Corthals G. L.; Schoenmakers P. J. A Cyclic-Olefin-Copolymer Microfluidic Immobilized-Enzyme Reactor for Rapid Digestion of Proteins from Dried Blood Spots. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 36.10.1016/j.chroma.2017.01.078. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

