The SAGA core module is critical during Drosophila oogenesis and is broadly recruited to promoters
- PMID: 34807910
- PMCID: PMC8648115
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009668
The SAGA core module is critical during Drosophila oogenesis and is broadly recruited to promoters
Abstract
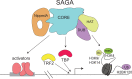
The Spt/Ada-Gcn5 Acetyltransferase (SAGA) coactivator complex has multiple modules with different enzymatic and non-enzymatic functions. How each module contributes to gene expression is not well understood. During Drosophila oogenesis, the enzymatic functions are not equally required, which may indicate that different genes require different enzymatic functions. An analogy for this phenomenon is the handyman principle: while a handyman has many tools, which tool he uses depends on what requires maintenance. Here we analyzed the role of the non-enzymatic core module during Drosophila oogenesis, which interacts with TBP. We show that depletion of SAGA-specific core subunits blocked egg chamber development at earlier stages than depletion of enzymatic subunits. These results, as well as additional genetic analyses, point to an interaction with TBP and suggest a differential role of SAGA modules at different promoter types. However, SAGA subunits co-occupied all promoter types of active genes in ChIP-seq and ChIP-nexus experiments, and the complex was not specifically associated with distinct promoter types in the ovary. The high-resolution genomic binding profiles were congruent with SAGA recruitment by activators upstream of the start site, and retention on chromatin by interactions with modified histones downstream of the start site. Our data illustrate that a distinct genetic requirement for specific components may conceal the fact that the entire complex is physically present and suggests that the biological context defines which module functions are critical.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was supported by funding from the Stowers Institute for Medical Research and a grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (R35GM118068) to Jerry L Workman. I have read the journal’s policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: J. Zeitlinger owns a patent on ChIP-nexus. Author Susan M. Abmayr was unable to confirm their authorship contributions. On their behalf, the corresponding author has reported their contributions to the best of their knowledge.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enzymatic modules of the SAGA chromatin-modifying complex play distinct roles in Drosophila gene expression and development.Genes Dev. 2017 Aug 1;31(15):1588-1600. doi: 10.1101/gad.300988.117. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Genes Dev. 2017. PMID: 28887412 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcription initiation function of the ubiquitous SAGA complex in tissue-specific gene activation.Genes Dev. 2011 Jul 15;25(14):1499-509. doi: 10.1101/gad.2046211. Genes Dev. 2011. PMID: 21764853 Free PMC article.
-
Differential requirement of SAGA components for recruitment of TATA-box-binding protein to promoters in vivo.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Nov;22(21):7365-71. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.21.7365-7371.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12370284 Free PMC article.
-
The Gcn5 complexes in Drosophila as a model for metazoa.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021 Feb;1864(2):194610. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194610. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021. PMID: 32735945 Review.
-
[SAGA complex: the role in viability and development].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2013 Nov-Dec;47(6):922-6. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2013. PMID: 25509853 Review. Russian.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

