Noninvasive Tape-Stripping with High-Resolution RNA Profiling Effectively Captures a Preinflammatory State in Nonlesional Psoriatic Skin
- PMID: 34808239
- PMCID: PMC9117571
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2021.09.038
Noninvasive Tape-Stripping with High-Resolution RNA Profiling Effectively Captures a Preinflammatory State in Nonlesional Psoriatic Skin
Abstract
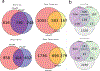
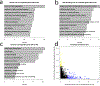
Tape stripping is a minimally invasive, nonscarring method that can be utilized to assess gene expression in the skin but is infrequently used given technical constraints. By comparing different tape stripping technologies and full-thickness skin biopsy results of lesional and nonlesional psoriatic skin from the same patients, we demonstrate that tape stripping with optimized high-resolution transcriptomic profiling can be used to effectively assess and characterize inflammatory responses in the skin. Upon comparison with single-cell RNA-sequencing data from psoriatic full-thickness skin biopsies, we illustrate that tape-stripping efficiently captures the transcriptome of the upper layers of the epidermis with sufficient resolution to assess the molecular components of the feed-forward immune amplification pathway in psoriasis. Notably, nonlesional psoriatic skin sampled by tape stripping demonstrates activated, proinflammatory changes when compared to healthy control skin, suggesting a prepsoriatic state, which is not captured on full-thickness skin biopsy transcriptome profiling. This work illustrates an approach to assess inflammatory response in the epidermis by combining noninvasive sampling with high throughput RNA-sequencing, providing a foundation for biomarker discoveries and mechanism of action studies for inflammatory skin conditions.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
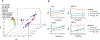


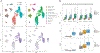
References
-
- Bata-Csorgo Z, Cooper KD, Ting KM, Voorhees JJ, Hammerberg C (1998) Fibronectin and alpha5 integrin regulate keratinocyte cell cycling. A mechanism for increased fibronectin potentiation of T cell lymphokine-driven keratinocyte hyperproliferation in psoriasis. J Clin Invest 101:1509–18. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buerger C, Richter B, Woth K, Salgo R, Malisiewicz B, Diehl S, et al. (2012) Interleukin-1beta interferes with epidermal homeostasis through induction of insulin resistance: implications for psoriasis pathogenesis. The Journal of investigative dermatology 132:2206–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

