Trend analysis of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria and antimicrobial consumption in the post-COVID-19 era: an extra challenge for healthcare institutions
- PMID: 34808311
- PMCID: PMC8603865
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhin.2021.11.011
Trend analysis of carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria and antimicrobial consumption in the post-COVID-19 era: an extra challenge for healthcare institutions
Abstract
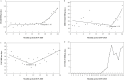
The incidence density trend of the carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria was analysed in device-associated infections and antimicrobial consumption in 99 critical care facilities in a low/middle-income country, between January 2019 and December 2020. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB) per 1000 patient-days increased in 2020 and this finding had a strong positive correlation with the incidence density of COVID-19 by the Spearman test. Polymyxin consumption also increased in 2020 but without significant correlation with CRAB or COVID-19 incidence density, presumably due to empirical and untargeted prescribing as a consequence of concern about CRAB infections. These findings are a warning to infection control programmes and antimicrobial stewardship.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; Antimicrobial drug resistance; COVID-19; Carbapenems; Healthcare-associated infections; Polymyxins.
Copyright © 2021 The Healthcare Infection Society. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on multidrug-resistant hospital-acquired bacterial infections.J Hosp Infect. 2022 May;123:191-192. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2022.02.015. Epub 2022 Mar 1. J Hosp Infect. 2022. PMID: 35245646 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Trends and correlation between antibacterial consumption and carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria in a tertiary hospital in China from 2012 to 2019.BMC Infect Dis. 2021 May 17;21(1):444. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06140-5. BMC Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34001022 Free PMC article.
-
[Impact of antimicrobial stewardship program on antimicrobial usage and detection rate of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Jul 2;57(7):553-558. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2019.07.012. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31269557 Chinese.
-
Carbapenem-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria-Related Healthcare-Associated Ventriculitis and Meningitis: Antimicrobial Resistance of the Pathogens, Treatment, and Outcome.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Jun 29;10(3):e0025322. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00253-22. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35467409 Free PMC article.
-
[Application progress of polymyxin in bloodstream infection of drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Nov;33(11):1401-1404. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210219-00255. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 34980319 Review. Chinese.
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of polymyxins based versus non-polymyxins based therapies in the infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Apr 21;20(1):296. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05026-2. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32316926 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Innovative Approaches to Monitor Central Line Associated Bloodstream Infections (CLABSIs) Bundle Efficacy in Intensive Care Unit (ICU): Role of Device Standardized Infection Rate (dSIR) and Standardized Utilization Ratio (SUR)-An Italian Experience.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 11;13(2):396. doi: 10.3390/jcm13020396. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38256530 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of COVID-19 pandemic on nosocomial multidrug-resistant bacterial bloodstream infections and antibiotic consumption in a tertiary care hospital.GMS Hyg Infect Control. 2022 Aug 29;17:Doc15. doi: 10.3205/dgkh000418. eCollection 2022. GMS Hyg Infect Control. 2022. PMID: 36157382 Free PMC article.
-
Rebound of Antibiotic Use and Respiratory Infections After Resumption of Normalcy From COVID-19 in Hong Kong.Infect Drug Resist. 2025 Mar 11;18:1325-1337. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S502126. eCollection 2025. Infect Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 40092846 Free PMC article.
-
Lipocalin-2 is an essential component of the innate immune response to Acinetobacter baumannii infection.PLoS Pathog. 2022 Sep 2;18(9):e1010809. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010809. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36054235 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) associated bacterial coinfection: Incidence, diagnosis and treatment.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2022 Dec;55(6 Pt 1):985-992. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2022.09.006. Epub 2022 Oct 7. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2022. PMID: 36243668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard. Available at: https://covid19.who.int/?gclid=Cj0KCQjwtMCKBhDAARIsAG-2Eu-HciJsbL9zoQLmR... [last accessed December 2021].
-
- Perez S., Innes G.K., Walters M.S., Mehr J., Arias J., Greeley R., et al. Increase in hospital-acquired carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii infection and colonization in an acute care hospital during a surge in COVID-19 admissions – New Jersey, February–July. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69:1827–1831. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6948e1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

