Integrated endotoxin-adsorption and antibacterial properties of platelet-membrane-coated copper silicate hollow microspheres for wound healing
- PMID: 34809612
- PMCID: PMC8607565
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-021-01130-w
Integrated endotoxin-adsorption and antibacterial properties of platelet-membrane-coated copper silicate hollow microspheres for wound healing
Abstract
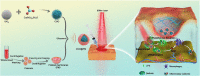
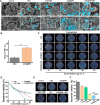
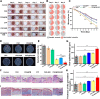
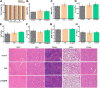
Serious infection caused by drug-resistant gram-negative bacteria and their secreted toxins (e.g., lipopolysaccharide) is a serious threat to human health. Thus, treatment strategies that efficiently kill bacteria and reducing the impact of their toxins simultaneously are urgently required. Herein, a novel antibacterial platform composed of a mesoporous copper silicate microsphere (CSO) core and a platelet membrane (PM) shell was prepared (CSO@PM). CSO@PM specifically targets bacteria owing to formyl peptide receptors on the PM and, combined with photothermal therapy (PTT), exhibits highly effective bacter icidal activity. Importantly, CSO@PM can adsorb lipopolysaccharide secreted by gram-negative bacteria, resulting in inflammation reduction. Thus, CSO@PM stimulates re-epithelialization and granulation-tissue formation, promoting wound healing. Moreover, this antibacterial platform exhibits no obvious toxicity at all the test concentrations in vitro and in vivo. Thus, CSO@PM exhibits a robust antibacterial effect and a strong toxin-adsorption capacity, facilitating the clinical treatment of many bacterial infections and the development of next-generation antibacterial nanoagents.
Keywords: Bacterial infection; Mesoporous copper silicate microspheres; Photothermal therapy; Toxin adsorption; Wound healing.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Sugden R, Kelly R, Davies S. Combatting antimicrobial resistance globally. Nat Microbiol. 2016;1(10):16187. - PubMed
-
- Herrera S, Bodro M, Soriano A. Predictors of multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa involvement in bloodstream infections. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2021. - PubMed
-
- Zumla A, Azhar EI, Hui DS, Shafi S, Petersen E, et al. Global spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria and mass-gathering religious events. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(5):488–490. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

