Nanoparticle-based delivery systems modulate the tumor microenvironment in pancreatic cancer for enhanced therapy
- PMID: 34809634
- PMCID: PMC8607729
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-021-01134-6
Nanoparticle-based delivery systems modulate the tumor microenvironment in pancreatic cancer for enhanced therapy
Abstract
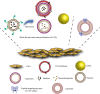
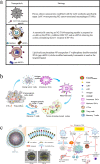
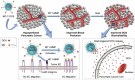
Pancreatic cancer is one of the most lethal malignant tumors with a low survival rate, partly because the tumor microenvironment (TME), which consists of extracellular matrix (ECM), cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), immune cells, and vascular systems, prevents effective drug delivery and chemoradiotherapy. Thus, modulating the microenvironment of pancreatic cancer is considered a promising therapeutic approach. Since nanoparticles are one of the most effective cancer treatment strategies, several nano-delivery platforms have been developed to regulate the TME and enhance treatment. Here, we summarize the latest advances in nano-delivery systems that alter the TME in pancreatic cancer by depleting ECM, inhibiting CAFs, reversing immunosuppression, promoting angiogenesis, or improving the hypoxic environment. We also discuss promising new targets for such systems. This review is expected to improve our understanding of how to modulate the pancreatic cancer microenvironment and guide the development of new therapies.
Keywords: Cancer-associated fibroblasts; Extracellular matrix; Immunosuppression; Nano-delivery systems; Pancreatic cancer; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

