The function role of ubiquitin proteasome pathway in the ER stress-induced AECII apoptosis during hyperoxia exposure
- PMID: 34809635
- PMCID: PMC8607682
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-021-01751-9
The function role of ubiquitin proteasome pathway in the ER stress-induced AECII apoptosis during hyperoxia exposure
Abstract
Background: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is a major cause of mortality and morbidity in premature infants, characterized by alveolar dysplasia and pulmonary microvascular remodeling. In the present study, we have investigated the functional roles of ubiquitin proteasome pathway (UPP) in BPD, and its relationship with endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) mediated type II alveolar epithelial cell (AECII) apoptosis.
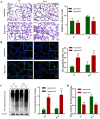
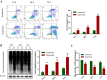
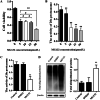
Methods: A hyperoxia-induced BPD rat model was constructed and the pathologic changes of lung tissues were evaluated by hematoxylin-eosin staining. Cell apoptosis and protein expression were determined by TUNEL assay and Western blotting, respectively. Further reagent kit with specific fluorescent substrate was utilized to measure the activity of 20 s proteasome. Meanwhile, AECII were cultured in vitro and exposed to hyperoxia. AECII apoptosis were measured by flow cytometry. In contrast, MG132 treatment was induced to explore UPP during hyperoxia exposure on AECII apoptosis and ERS sensors expression.
Results: A significant increase in apoptosis and total ubiquitinated proteins expression were observed in BPD rats and AECII culture, and the change of UPP was associated with ERS. In order to confirm the role of UPP in AECII apoptosis of BPD, AECII cells were treated by MG132 with the concentration of 10 μmol/L under hyperoxia exposure. We found that the proteins expression of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP-78), PKR-like ER kinase (PERK), activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4), activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) and C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), as well as AECII apoptosis were increased following MG132 treatment. Furthermore, the relatively up-regulated in the levels of total ubiquitinated proteins expression and 20 s proteasome activity were correlated with increased ERS sensors expression.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that UPP may participate in the ERS-induced AECII apoptosis under hyperoxia condition.
Keywords: Alveolar epithelial type II cells; Apoptosis; Bronchopulmonary dysplasia; Endoplasmic reticulum stress; Ubiquitin proteasome pathway.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
Figures



References
-
- Tanaka T, Saito Y, Matsuda K, Kamio K, Abe S, Kubota K, Azuma A, Gemma A. Cyclic mechanical stretch-induced oxidative stress occurs via a NOX-dependent mechanism in type II alveolar epithelial cells. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2017;242:108–116. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

