TMPRSS4 promotes cancer stem-like properties in prostate cancer cells through upregulation of SOX2 by SLUG and TWIST1
- PMID: 34809669
- PMCID: PMC8607621
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-021-02147-7
TMPRSS4 promotes cancer stem-like properties in prostate cancer cells through upregulation of SOX2 by SLUG and TWIST1
Abstract
Background: Transmembrane serine protease 4 (TMPRSS4) is a cell surface-anchored serine protease. Elevated expression of TMPRSS4 correlates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer, gastric cancer, prostate cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, and other cancers. Previously, we demonstrated that TMPRSS4 promotes invasion and proliferation of prostate cancer cells. Here, we investigated whether TMPRSS4 confers cancer stem-like properties to prostate cancer cells and characterized the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Acquisition of cancer stem-like properties by TMPRSS4 was examined by monitoring anchorage-independent growth, tumorsphere formation, aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) activation, and resistance to anoikis and drugs in vitro and in an early metastasis model in vivo. The underlying molecular mechanisms were evaluated, focusing on stemness-related factors regulated by epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-inducing transcription factors. Clinical expression and significance of TMPRSS4 and stemness-associated factors were explored by analyzing datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA).
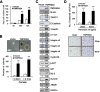
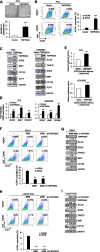
Results: TMPRSS4 promoted anchorage-independent growth, ALDH activation, tumorsphere formation, and therapeutic resistance of prostate cancer cells. In addition, TMPRSS4 promoted resistance to anoikis, thereby increasing survival of circulating tumor cells and promoting early metastasis. These features were accompanied by upregulation of stemness-related factors such as SOX2, BMI1, and CD133. SLUG and TWIST1, master EMT-inducing transcription factors, made essential contributions to TMPRSS4-mediated cancer stem cell (CSC) features through upregulation of SOX2. SLUG stabilized SOX2 via preventing proteasomal degradation through its interaction with SOX2, while TWIST1 upregulated transcription of SOX2 by interacting with the proximal E-box element in the SOX2 promoter. Clinical data showed that TMPRSS4 expression correlated with the levels of SOX2, PROM1, SNAI2, and TWIST1. Expression of SOX2 was positively correlated with that of TWIST1, but not with other EMT-inducing transcription factors, in various cancer cell lines.
Conclusions: Together, these findings suggest that TMPRSS4 promotes CSC features in prostate cancer through upregulation of the SLUG- and TWIST1-induced stem cell factor SOX2 beyond EMT. Thus, TMPRSS4/SLUG-TWIST1/SOX2 axis may represent a novel mechanism involved in the control of tumor progression.
Keywords: SLUG; SOX2; Stemness; TMPRSS4; TWIST1.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
TMPRSS4 induces invasion and proliferation of prostate cancer cells through induction of Slug and cyclin D1.Oncotarget. 2016 Aug 2;7(31):50315-50332. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10382. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27385093 Free PMC article.
-
TMPRSS4 Upregulates TWIST1 Expression through STAT3 Activation to Induce Prostate Cancer Cell Migration.Pathol Oncol Res. 2018 Apr;24(2):251-257. doi: 10.1007/s12253-017-0237-z. Epub 2017 May 2. Pathol Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 28466252
-
VEGFA links self-renewal and metastasis by inducing Sox2 to repress miR-452, driving Slug.Oncogene. 2017 Sep 7;36(36):5199-5211. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.4. Epub 2017 May 15. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 28504716 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness: the Twist1-Bmi1 connection.Biosci Rep. 2011 Dec;31(6):449-55. doi: 10.1042/BSR20100114. Biosci Rep. 2011. PMID: 21919891 Review.
-
Yin Yang 1 is associated with cancer stem cell transcription factors (SOX2, OCT4, BMI1) and clinical implication.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 May 25;35:84. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0359-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27225481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic effects of TM4SF5-targeting chimeric and humanized monoclonal antibodies in hepatocellular and colon cancer models.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2022 Jan 31;24:452-466. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2022.01.006. eCollection 2022 Mar 17. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2022. PMID: 35211652 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a prognostic model for anoikis and identifies hub genes in hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 7;13(1):14723. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41139-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37679418 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Biology of Prostate Cancer Stem Cells: From the Past to the Future.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 19;24(8):7482. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087482. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EphA2 promotes the transcription of KLF4 to facilitate stemness in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jun 25;81(1):278. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05325-w. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38916835 Free PMC article.
-
TMPRSS4, a type II transmembrane serine protease, as a potential therapeutic target in cancer.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Apr;55(4):716-724. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-00975-5. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37009799 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 2011;331(6024):1559–1564. - PubMed
-
- Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139(5):871–890. - PubMed
-
- Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A. Snail, Zeb and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(6):415–428. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

