Transcriptional landscape of highly lignified poplar stems at single-cell resolution
- PMID: 34809675
- PMCID: PMC8607660
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-021-02537-2
Transcriptional landscape of highly lignified poplar stems at single-cell resolution
Abstract
Background: Plant secondary growth depends on the activity of the vascular cambium, which produces xylem and phloem. Wood derived from xylem is the most abundant form of biomass globally and has played key socio-economic and subsistence roles throughout human history. However, despite intensive study of vascular development, the full diversity of cell types and the gene networks engaged are still poorly understood.
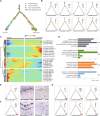
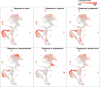
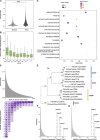
Results: Here, we have applied an optimized protoplast isolation protocol and RNA sequencing to characterize the high-resolution single-cell transcriptional landscape of highly lignified poplar stems. We identify 20 putative cell clusters with a series of novel cluster-specific marker genes and find that these cells are highly heterogeneous based on the transcriptome. Analysis of these marker genes' expression dynamics enables reconstruction of the cell differentiation trajectories involved in phloem and xylem development. We find that different cell clusters exhibit distinct patterns of phytohormone responses and emphasize the use of our data to predict potential gene redundancy and identify candidate genes related to vascular development in trees.
Conclusions: These findings establish the transcriptional landscape of major cell types of poplar stems at single-cell resolution and provide a valuable resource for investigating basic principles of vascular cell specification and differentiation in trees.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Merit of integrating in situ transcriptomics and anatomical information for cell annotation and lineage construction in single-cell analyses of Populus.Genome Biol. 2024 Apr 3;25(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13059-024-03227-5. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 38570851 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

