Disrupting Roquin-1 interaction with Regnase-1 induces autoimmunity and enhances antitumor responses
- PMID: 34811541
- PMCID: PMC8996344
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-021-01064-3
Disrupting Roquin-1 interaction with Regnase-1 induces autoimmunity and enhances antitumor responses
Abstract
Roquin and Regnase-1 proteins bind and post-transcriptionally regulate proinflammatory target messenger RNAs to maintain immune homeostasis. Either the sanroque mutation in Roquin-1 or loss of Regnase-1 cause systemic lupus erythematosus-like phenotypes. Analyzing mice with T cells that lack expression of Roquin-1, its paralog Roquin-2 and Regnase-1 proteins, we detect overlapping or unique phenotypes by comparing individual and combined inactivation. These comprised spontaneous activation, metabolic reprogramming and persistence of T cells leading to autoimmunity. Here, we define an interaction surface in Roquin-1 for binding to Regnase-1 that included the sanroque residue. Mutations in Roquin-1 impairing this interaction and cooperative regulation of targets induced T follicular helper cells, germinal center B cells and autoantibody formation. These mutations also improved the functionality of tumor-specific T cells by promoting their accumulation in the tumor and reducing expression of exhaustion markers. Our data reveal the physical interaction of Roquin-1 with Regnase-1 as a hub to control self-reactivity and effector functions in immune cell therapies.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures




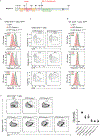


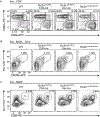







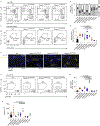

References
-
- Pratama A et al. Roquin-2 shares functions with its paralog Roquin-1 in the repression of mRNAs controlling T follicular helper cells and systemic inflammation. Immunity 38, 669–680 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Vogel KU et al. Roquin paralogs 1 and 2 redundantly repress the Icos and Ox40 costimulator mRNAs and control follicular helper T cell differentiation. Immunity 38, 655–668 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Matsushita K et al. Zc3h12a is an RNase essential for controlling immune responses by regulating mRNA decay. Nature 458, 1185–1190 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Uehata T et al. Malt1-induced cleavage of regnase-1 in CD4+ helper T cells regulates immune activation. Cell 153, 1036–1049 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

