Cross-reactive antibodies after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination
- PMID: 34812143
- PMCID: PMC8610423
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.70330
Cross-reactive antibodies after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination
Abstract
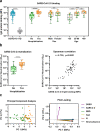
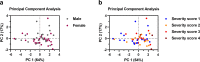
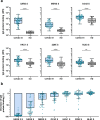
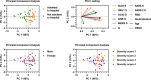
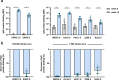
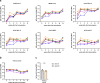
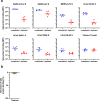
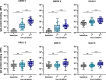
Current SARS-CoV-2 vaccines are losing efficacy against emerging variants and may not protect against future novel coronavirus outbreaks, emphasizing the need for more broadly protective vaccines. To inform the development of a pan-coronavirus vaccine, we investigated the presence and specificity of cross-reactive antibodies against the spike (S) proteins of human coronaviruses (hCoV) after SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination. We found an 11- to 123-fold increase in antibodies binding to SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV as well as a 2- to 4-fold difference in antibodies binding to seasonal hCoVs in COVID-19 convalescent sera compared to pre-pandemic healthy donors, with the S2 subdomain of the S protein being the main target for cross-reactivity. In addition, we detected cross-reactive antibodies to all hCoV S proteins after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in macaques and humans, with higher responses for hCoV more closely related to SARS-CoV-2. These findings support the feasibility of and provide guidance for development of a pan-coronavirus vaccine.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibodies; coronavirus; cross-reactivity; human; immunology; infectious disease; inflammation; microbiology; vaccine.
© 2021, Grobben et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MG, Kv, PB, MB, PM, ND, BA, AL, Lv, JB, MP, MO, DE, TB, Hv, EW, BV, OF, Pd, TB, MB, JS, RL, Md, MP, AC, Gd, RS, Mv No competing interests declared
Figures



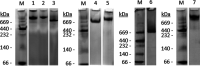

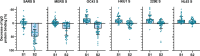
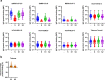
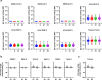
References
-
- Anderson EM, Goodwin EC, Verma A, Arevalo CP, Bolton MJ, Weirick ME, Gouma S, McAllister CM, Christensen SR, Weaver J, Hicks P, Manzoni TB, Oniyide O, Ramage H, Mathew D, Baxter AE, Oldridge DA, Greenplate AR, Wu JE, Alanio C, D’Andrea K, Kuthuru O, Dougherty J, Pattekar A, Kim J, Han N, Apostolidis SA, Huang AC, Vella LA, Kuri-Cervantes L, Pampena MB, UPenn COVID Processing Unit. Betts MR, Wherry EJ, Meyer NJ, Cherry S, Bates P, Rader DJ, Hensley SE. Seasonal human coronavirus antibodies are boosted upon SARS-CoV-2 infection but not associated with protection. Cell. 2021;184:1858–1864. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Appelman B, van der Straten K, Lavell AHA, Schinkel M, Slim MA, Poniman M, Burger JA, Oomen M, Tejjani K, Vlaar APJ, Wiersinga WJ, Smulders YM, van Vught LA, Sanders RW, van Gils MJ, Bomers MK, Sikkens JJ, Amsterdam UMC COVID-19 S3/HCW study group Time since SARS-CoV-2 infection and humoral immune response following BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination. EBioMedicine. 2021;72:103589. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103589. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baden LR, El Sahly HM, Essink B, Kotloff K, Frey S, Novak R, Diemert D, Spector SA, Rouphael N, Creech CB, McGettigan J, Khetan S, Segall N, Solis J, Brosz A, Fierro C, Schwartz H, Neuzil K, Corey L, Gilbert P, Janes H, Follmann D, Marovich M, Mascola J, Polakowski L, Ledgerwood J, Graham BS, Bennett H, Pajon R, Knightly C, Leav B, Deng W, Zhou H, Han S, Ivarsson M, Miller J, Zaks T, COVE Study Group Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2021;384:403–416. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2035389. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

