Immune system cells from COVID-19 patients display compromised mitochondrial-nuclear expression co-regulation and rewiring toward glycolysis
- PMID: 34812416
- PMCID: PMC8599136
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103471
Immune system cells from COVID-19 patients display compromised mitochondrial-nuclear expression co-regulation and rewiring toward glycolysis
Abstract
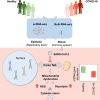
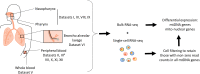
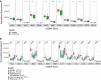
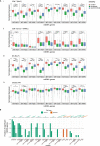
Mitochondria are pivotal for bioenergetics, as well as in cellular response to viral infections. Nevertheless, their role in COVID-19 was largely overlooked. Here, we analyzed available bulk RNA-seq datasets from COVID-19 patients and corresponding healthy controls (three blood datasets, N = 48 healthy, 119 patients; two respiratory tract datasets, N = 157 healthy, 524 patients). We found significantly reduced mtDNA gene expression in blood, but not in respiratory tract samples from patients. Next, analysis of eight single-cells RNA-seq datasets from peripheral blood mononuclear cells, nasopharyngeal samples, and Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (N = 1,192,243 cells), revealed significantly reduced mtDNA gene expression especially in immune system cells from patients. This is associated with elevated expression of nuclear DNA-encoded OXPHOS subunits, suggesting compromised mitochondrial-nuclear co-regulation. This, together with elevated expression of ROS-response genes and glycolysis enzymes in patients, suggest rewiring toward glycolysis, thus generating beneficial conditions for SARS-CoV-2 replication. Our findings underline the centrality of mitochondrial dysfunction in COVID-19.
Keywords: Genomics; Immune system; Virology.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests. The manuscript is based on analyses of publicly available data. The source of each dataset is mentioned within the STAR Methods section.
Figures

References
-
- Al Amir Dache Z., Otandault A., Tanos R., Pastor B., Meddeb R., Sanchez C., Arena G., Lasorsa L., Bennett A., Grange T., et al. Blood contains circulating cell-free respiratory competent mitochondria. FASEB. 2020;34:3616–3630. - PubMed
-
- Ardail D., Lerme F., Puymirat J., Morel G. Evidence for the presence of alpha and beta-related T3 receptors in rat liver mitochondria. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1993;62:105–113. - PubMed
-
- Ballestar E., Farber D.L., Glover S., Horwitz B., Meyer K., Nikolić M., Ordovas-Montanes J., Sims P., Shalek A., Vandamme N., et al. Single cell profiling of COVID-19 patients: an international data resource from multiple tissues. medrxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.11.20.20227355. - DOI
-
- Bernardes J.P., Mishra N., Tran F., Bahmer T., Best L., Blase J.I., Bordoni D., Franzenburg J., Geisen U., Josephs-Spaulding J., et al. Longitudinal multi-omics analyses identify responses of megakaryocytes, erythroid cells, and plasmablasts as hallmarks of severe COVID-19. Immunity. 2020;53:1296–1314 e9. - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

