Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of the Plasma Proteome in Black Adults Provides Novel Insights Into Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 34814699
- PMCID: PMC9158509
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.055117
Whole Genome Sequence Analysis of the Plasma Proteome in Black Adults Provides Novel Insights Into Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
Background: Plasma proteins are critical mediators of cardiovascular processes and are the targets of many drugs. Previous efforts to characterize the genetic architecture of the plasma proteome have been limited by a focus on individuals of European descent and leveraged genotyping arrays and imputation. Here we describe whole genome sequence analysis of the plasma proteome in individuals with greater African ancestry, increasing our power to identify novel genetic determinants.
Methods: Proteomic profiling of 1301 proteins was performed in 1852 Black adults from the Jackson Heart Study using aptamer-based proteomics (SomaScan). Whole genome sequencing association analysis was ascertained for all variants with minor allele count ≥5. Results were validated using an alternative, antibody-based, proteomic platform (Olink) as well as replicated in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis and the HERITAGE Family Study (Health, Risk Factors, Exercise Training and Genetics).
Results: We identify 569 genetic associations between 479 proteins and 438 unique genetic regions at a Bonferroni-adjusted significance level of 3.8×10-11. These associations include 114 novel locus-protein relationships and an additional 217 novel sentinel variant-protein relationships. Novel cardiovascular findings include new protein associations at the APOE gene locus including ZAP70 (sentinel single nucleotide polymorphism [SNP] rs7412-T, β=0.61±0.05, P=3.27×10-30) and MMP-3 (β=-0.60±0.05, P=1.67×10-32), as well as a completely novel pleiotropic locus at the HPX gene, associated with 9 proteins. Further, the associations suggest new mechanisms of genetically mediated cardiovascular disease linked to African ancestry; we identify a novel association between variants linked to APOL1-associated chronic kidney and heart disease and the protein CKAP2 (rs73885319-G, β=0.34±0.04, P=1.34×10-17) as well as an association between ATTR amyloidosis and RBP4 levels in community-dwelling individuals without heart failure.
Conclusions: Taken together, these results provide evidence for the functional importance of variants in non-European populations, and suggest new biological mechanisms for ancestry-specific determinants of lipids, coagulation, and myocardial function.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; genetics; proteomics; race and ethnicity.
Figures


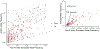

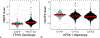
Comment in
-
Linking Genetics and Proteomics: Gene-Protein Associations Built on Diversity.Circulation. 2022 Feb;145(5):371-374. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.121.058303. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Circulation. 2022. PMID: 35100019 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100037C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00001/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095167/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL142711/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000040/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM118430/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00002/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NR019628/NR/NINR NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095161/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00005/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095168/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD029586/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003067/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL047327/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG059898/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR002542/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095169/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL047323/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800014I/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800014C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095159/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL141601/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG063507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800013I/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800012I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL161259/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001420/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX001737/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- 75N92020D00004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL132320/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00007/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095163/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG052409/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL133870/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201500003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007374/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800015I/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095166/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 HL150992/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800010I/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA154274/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX005831/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- R01 HL047317/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92020D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095162/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800011I/HB/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095165/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095164/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K23 DK127073/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146462/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL145095/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL045670/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC095160/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

