The role of MAPK11/12/13/14 (p38 MAPK) protein in dopamine agonist-resistant prolactinomas
- PMID: 34814904
- PMCID: PMC8609849
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-021-00900-9
The role of MAPK11/12/13/14 (p38 MAPK) protein in dopamine agonist-resistant prolactinomas
Abstract
Background: Prolactinoma is a functional pituitary adenoma that secretes excessive prolactin. Dopamine agonists (DAs) such as bromocriptine (BRC) are the first-line treatment for prolactinomas, but the resistance rate is increasing year by year, creating a clinical challenge. Therefore, it is urgent to explore the molecular mechanism of bromocriptine resistance in prolactinomas. Activation of the P38 MAPK pathway affects multidrug resistance in tumours. Our previous studies have demonstrated that inhibiting MAPK14 can suppress the occurrence of prolactinoma, but the role of MAPK11/12/13/14 (p38 MAPK) signalling in dopamine agonist-resistant prolactinomas is still unclear.
Methods: A prolactinoma rat model was established to determine the effect of bromocriptine on MAPK11/12/13/14 signalling. DA-resistant GH3 cells and DA-sensitive MMQ cells were used, and the role of MAPK11/12/13/14 in bromocriptine-resistant prolactinomas was preliminarily verified by western blot, RT-qPCR, ELISA, flow cytometry and CCK-8 experiments. The effects of MAPK11 or MAPK14 on bromocriptine-resistant prolactinomas were further verified by siRNA transfection experiments.
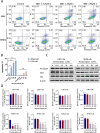
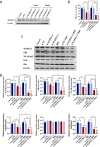
Results: Bromocriptine was used to treat rat prolactinoma by upregulating DRD2 expression and downregulating the expression level of MAPK11/12/13/14 in vivo experiments. The in vitro experiments showed that GH3 cells are resistant to bromocriptine and that MMQ cells are sensitive to bromocriptine. Bromocriptine could significantly reduce the expression of MAPK12 and MAPK13 in GH3 cells and MMQ cells. Bromocriptine could significantly reduce the expression of MAPK11, MAPK14, NF-κB p65 and Bcl2 in MMQ but had no effect on MAPK11, MAPK14, NF-κB p65 and Bcl2 in GH3 cells. In addition, knockdown of MAPK11 and MAPK14 in GH3 cells by siRNA transfection reversed the resistance of GH3 cells to bromocriptine, and haloperidol (HAL) blocked the inhibitory effect of bromocriptine on MAPK14, MAPK11, and PRL in MMQ cells. Our findings show that MAPK11 and MAPK14 proteins are involved in bromocriptine resistance in prolactinomas.
Conclusion: Bromocriptine reduces the expression of MAPK11/12/13/14 in prolactinomas, and MAPK11 and MAPK14 are involved in bromocriptine resistance in prolactinomas by regulating apoptosis. Reducing the expression of MAPK11 or MAPK14 can reverse bromocriptine resistance in prolactinomas.
Keywords: Bromocriptine; Dopamine agonist; Drug resistance; MAPK11/12/13/14; Prolactinomas.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Inhibiting MAPK14 showed anti-prolactinoma effect.BMC Endocr Disord. 2020 Sep 7;20(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12902-020-00619-z. BMC Endocr Disord. 2020. PMID: 32894113 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin Sensitizes Prolactinoma Cells to Bromocriptine by Activating the ERK/EGR1 and Inhibiting the AKT/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway In Vitro and In Vivo.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Dec;58(12):6170-6185. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02541-4. Epub 2021 Aug 31. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34463926
-
The role of TGF-β/Smad signaling in dopamine agonist-resistant prolactinomas.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Feb 15;402:64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.12.024. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 25578603
-
Diagnosis and drug therapy of prolactinoma.Drugs. 1996 Jun;51(6):954-65. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199651060-00004. Drugs. 1996. PMID: 8736617 Review.
-
Management of Dopamine Agonist-Resistant Prolactinoma.Neuroendocrinology. 2019;109(1):42-50. doi: 10.1159/000495775. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Neuroendocrinology. 2019. PMID: 30481756 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurotransmitters: an emerging target for therapeutic resistance to tumor immune checkpoint inhibitors.Mol Cancer. 2025 Aug 11;24(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02413-8. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40790592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

