Discoidin Domain Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 1 (DDR1): A Novel Predictor for Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Curative Resection
- PMID: 34815375
- PMCID: PMC8628480
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.933109
Discoidin Domain Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 1 (DDR1): A Novel Predictor for Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Curative Resection
Abstract
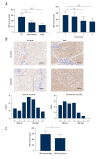
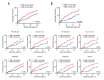
BACKGROUND Previous studies showed that the discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1 (DDR1) is significantly elevated in a variety of cancers, and it is closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors. However, its clinical significance in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is not fully elucidated. So, in this study, we aimed to systemically evaluate the prognostic value of DDR1 in HCC. MATERIAL AND METHODS A total of 200 individuals were enrolled in this study (including 120 HCC patients, 40 chronic hepatitis patients, and 40 health individuals). The contents of DDR1 in serum was measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), while the expression level of DDR1 in para-tumor and tumor tissue was detected by immunohistochemistry staining. Kaplan-Meier, Cox regression analyses, and log-rank test were used to assess the prognostic value. RESULTS The contents of DDR1 in serum of HCC patients was significantly higher compared with chronic hepatitis patients (P<0.01) and health individuals (P<0.001). The expression level of DDR1 in tumors was higher than that in normal liver tissue, and it had relatively strong correlation with DDR1 in serum. We next demonstrated that high DDR1 has utility as a prognostic risk factor for tumor recurrence and metastasis, and it still retains its discrimination ability in low-risk groups (BCLC 0+A). Moreover, DDR1 is as an independent predictor of prognosis in HCC patients with microvascular invasion (MVI), and is strongly associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related protein. CONCLUSIONS DDR1 is a novel predictor for HCC recurrence. Integration of serum and tumor DDR1 detection into clinical management would provide convenience and enhanced accuracy in clinical practice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
DDR1 is a Novel Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target for the Combination Treatment of Liver Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241286257. doi: 10.1177/10732748241286257. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 39284684 Free PMC article.
-
The cross-talk between DDR1 and STAT3 promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Jul 27;12(14):14391-14405. doi: 10.18632/aging.103482. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. Retraction in: Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Sep 15;16(17):12429-12430. doi: 10.18632/aging.205988. PMID: 32716315 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
DDR1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through recruiting PSD4 to ARF6.Oncogene. 2022 Mar;41(12):1821-1834. doi: 10.1038/s41388-022-02212-1. Epub 2022 Feb 9. Oncogene. 2022. PMID: 35140331 Free PMC article.
-
Discoidin Domain Receptor 1, a Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Feb 23;15:2037-2044. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S348110. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35237068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Research Progress of Discoidin Domain Receptor 1 in Breast Cancer and Other Malignant Tumors].Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2021 Aug;43(4):634-641. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.13315. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34494537 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Focusing on discoidin domain receptors in premalignant and malignant liver diseases.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 15;13:1123638. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1123638. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37007062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging strategies and translational advancements of DDR1 in oncology.Discov Oncol. 2025 Mar 30;16(1):428. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02107-z. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40159417 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Overexpression of CLEC5A inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis and reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023 Jan 20;43(1):85-91. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2023.01.11. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2023. PMID: 36856214 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Roles and Molecular Mechanisms of Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma with Microvascular Invasion: A Review.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023 Oct 28;11(5):1170-1183. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00013S. Epub 2023 May 4. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 37577231 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bruix J, Reig M, Sherman M. Evidence-based diagnosis, staging, and treatment of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2016;150:835–53. - PubMed
-
- Galle PR, Tovoli F, Foerster F, et al. The treatment of intermediate stage tumours beyond TACE: from surgery to systemic therapy. J Hepatol. 2017;67:173–83. - PubMed
-
- Shrivastava A, Radziejewski C, Campbell E, et al. An orphan receptor tyrosine kinase family whose members serve as nonintegrin collagen receptors. Mol Cell. 1997;1:25–34. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

